-
Review Article
- Improvement of oocyte in vitro maturation for assisted reproductive technology application in mammal
- Adel R. Moawad, Inchul Choi
- In vitro maturation (IVM) of mammalian oocytes is one of the earliest achievements in reproductive biology, first demonstrated in mice and later …
- In vitro maturation (IVM) of mammalian oocytes is one of the earliest achievements in reproductive biology, first demonstrated in mice and later extended to livestock and humans. While extrusion of the first polar body is a common marker of nuclear maturation, full developmental competence also requires cytoplasmic changes such as mitochondrial redistribution, maternal RNA regulation, cytoskeletal remodeling, and redox balance. The importance of IVM differs by field. In livestock, it underpins in vitro embryo production (IVP) from slaughterhouse ovaries or ovum pick-up, and provides essential oocytes for embryo transfer, somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT), and genome editing. In humans, IVM reduces the need for strong ovarian stimulation, lowering the risk of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Furthermore, climate change and heat stress in dairy cattle highlight IVM as a strategy to maintain oocyte quality under controlled conditions. However, IVM-derived oocytes still show reduced competence compared with those that mature in vivo, largely due to incomplete cytoplasmic maturation, such as clustered mitochondrial distribution and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. To overcome these limitations, several strategies have been developed, including antioxidant supplementation in culture media, co-culture systems, and microfluidic platforms. In particular, the integration of IVM with vitrification has further expanded assisted reproductive technology (ART). In this review, we focus on evaluation methods for oocyte maturation, improved culture approaches, integration with cryopreservation, and applications in ART and biotechnology, including IVP, SCNT, and genome editing. - COLLAPSE
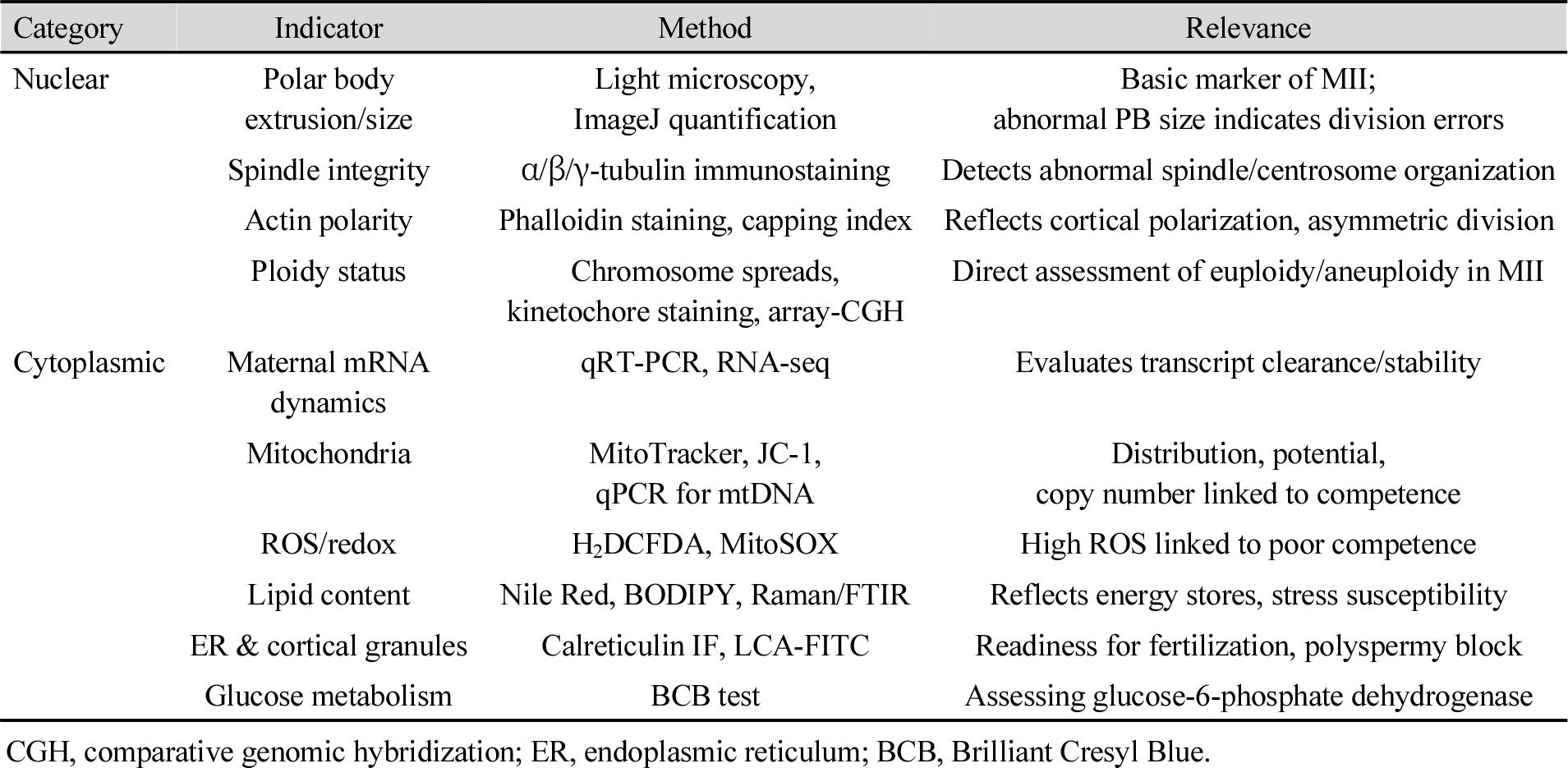
-
Review Article
- Role of apoptosis and anti-apoptosis mechanism in meat quality: An integrated mechanistic review of tenderness development
- Jong Ho Lee, Traci Alexandra Cramer, Dylan Dragon Metzel, Yuan H. Brad Kim
- Muscle-to-meat conversion is a complex process that determines final meat quality, which in turn influences consumer preference and repurchasing decisions. Traditionally, this …
- Muscle-to-meat conversion is a complex process that determines final meat quality, which in turn influences consumer preference and repurchasing decisions. Traditionally, this conversion process has been explained through the calpain system, but it has a limited ability to account for changes in muscle type, various stress conditions, and breed-specific differences. Recent research has consistently demonstrated that apoptosis initiates this conversion. Therefore, this review proposes apoptosis as a key mechanism regulating postmortem muscle changes, and it introduces an integrated model to explain the complex conversion process. Apoptosis is triggered by hypoxia, energy depletion, and oxidative stress in postmortem muscle. This process is regulated by increased mitochondrial outer membrane permeability, cytochrome c release, and an increase in the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio. Caspases activated by these events degrade structural proteins and calpastatin. However, this apoptotic process may potentially be inhibited by heat shock proteins and endogenous antioxidant enzymes. While apoptosis may contribute to tenderization, it can induce cell shrinkage and mitochondrial damage, which can also negatively impact meat quality attributes such as water-holding capacity and color stability. This integrated understanding can explain complex phenomena such as muscle-specific variations and the differential impacts of antemortem versus postmortem stress. Therefore, this framework is expected to form the basis for new industrial strategies to improve meat quality. - COLLAPSE
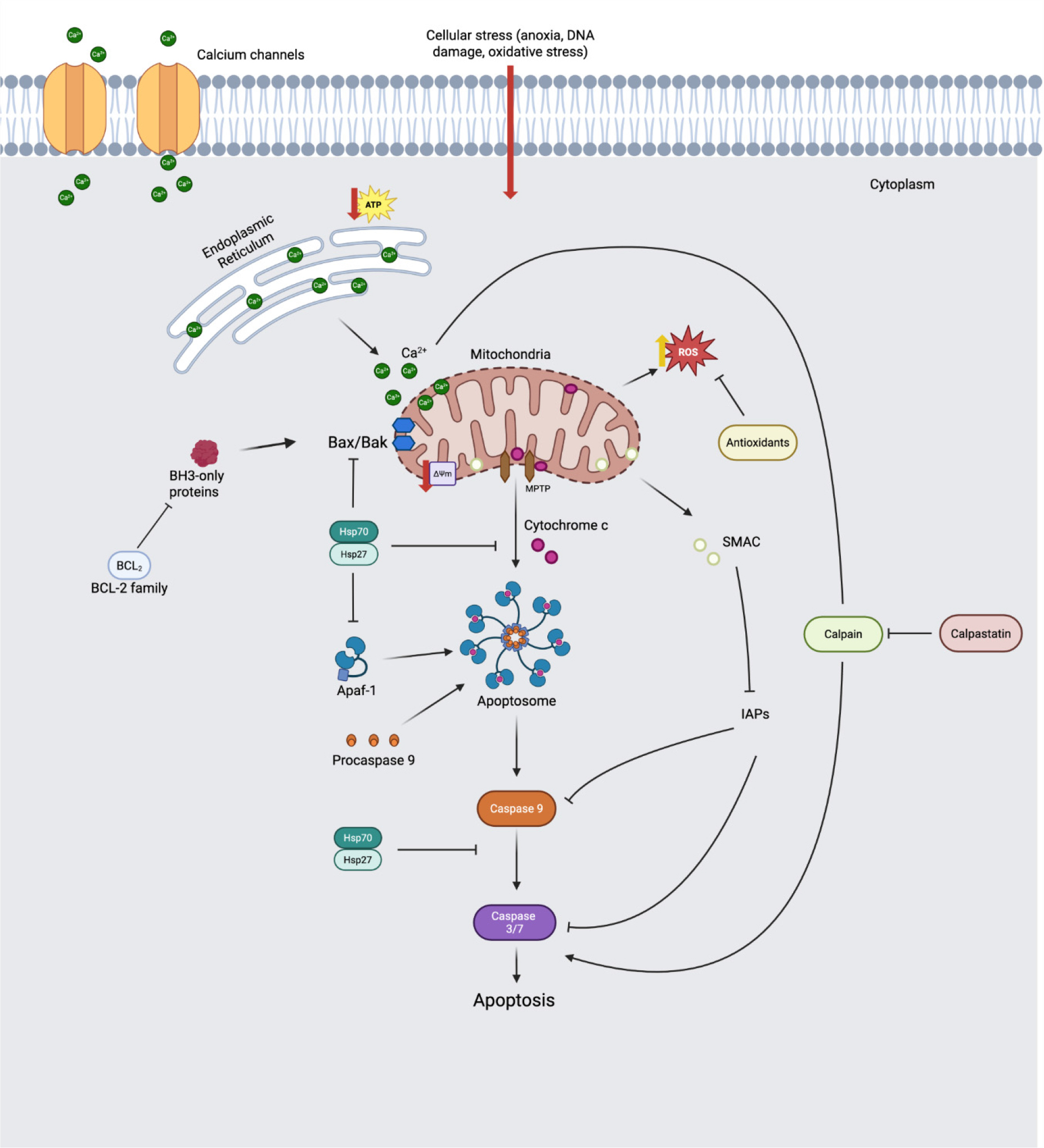
-
Food & Chemistry
- Identifying an accurate and efficient approach to soil organic matter removal for quantifying microplastics in agricultural soils
- Yun-Gu Kang, Jiwon Choi, Jun-Yeong Lee, Ji-Hoon Kim, Jun-Ho Kim, Taek-Keun Oh
- For efficient microplastic (MP) separation, there is a need to remove the soil organic matter (SOM), which interferes with MP extraction. However, …
- For efficient microplastic (MP) separation, there is a need to remove the soil organic matter (SOM), which interferes with MP extraction. However, the efficient SOM removal strategy from agricultural soils remain under debate. Therefore, this study investigated the SOM decomposition efficiency and MP recovery yield under varying environmental temperatures (i.e., 0, 20, and 40℃) conditions using five different removal solutions in three types of agricultural soil (i.e., upland, orchard, and greenhouse soils). Considering the thermal sensitivity and characteristics of MP samples, the study aimed to identify pre-treatment conditions that effectively decompose SOM content without significantly compromising MP recovery yield. Soil samples containing 1% (w/w) polystyrene (PS) particles were subjected to distilled water, acid-digestion (HNO3), alkaline-digestion (KOH), and oxidative (H2O2 and Fenton [H2O2 + FeSO4]) treatments, followed by density-separation using NaCl solution (1.21 g·cm-3), and the PS recovery rate was quantified after oven-drying. The SOM decomposition accelerated with increasing environmental temperature, and the its highest efficiency, which reduced SOM content by 44, 36, and 29%, were observed in the Fenton reagent-applied upland, orchard, and greenhouse soils, respectively. The MP recovery rates were positively correlated with SOM decomposition efficiency, and the oxidation reaction consistently yielded higher MP recovery yield than other approaches. However, the H2O2 treatment led to variable MP losses, particularly in low-organic soils, suggesting possible MP degradation during excessive oxidation. Hence, treating agricultural soil with the Fenton reagent at 40℃ condition was found to be the most effective strategy for decomposing SOM content while maintaining MP integrity. - COLLAPSE

-
Engineering
- Simulation of the power transmission durability for a 20 kW single motor driving electric tractor
- Dong Wook Kim, Ji Hun Yu, Jong Dae Park, Min Jong Park, Yong Joo Kim
- This study aimed to develop a simulation model and validate the durability of a 20-kW electric tractor power transmission. Power transmission consisted …
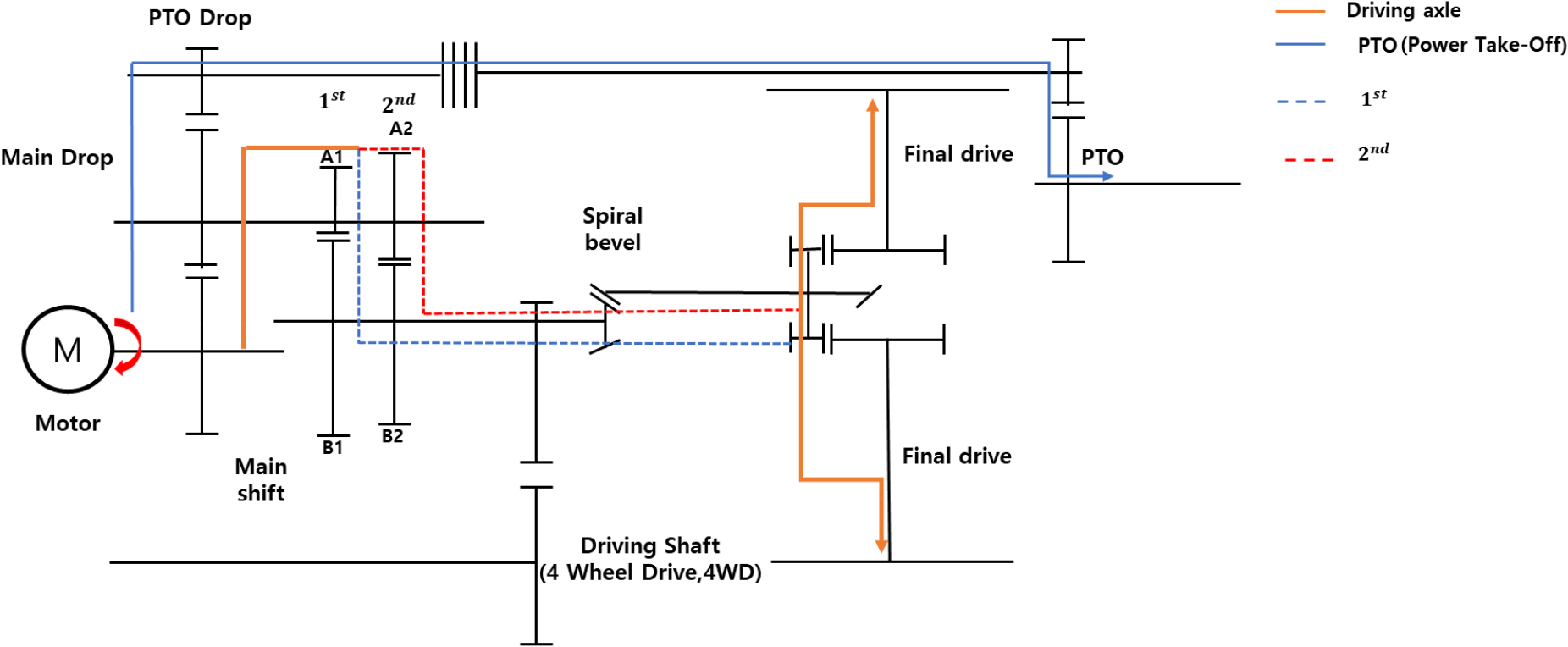
- This study aimed to develop a simulation model and validate the durability of a 20-kW electric tractor power transmission. Power transmission consisted of a motor, transmission, axle and wheels. The transmission simulation model was developed using MASTA, a gear analysis software, and motor rotational speed, as well as wheel and power take-off (PTO) torque generated during agricultural work were applied as input parameters of the simulation model. The safety factors of the gears and bearing damage were analyzed. The power transmission durability test was conducted using a dynamometer. The input motor speed was adjusted by the input speed, and the load motor torque was adjusted by applied the load under test conditions. Zero-failure test times were 2,418 hours, whereas acceleration life testing (ALT) was approximately 160 hours using the dynamometer. The gear safety analysis results showed that the bending safety factor of the pinion in spiral bevel gear was 1.19 and the contact safety factor was also 1.12 which was the lowest among all gear pairs. The bearing safety analysis showed that the highest bearing damage rate was 58.69%, and the lowest safety factor of 1.30. Gear and bearing analysis results of the powertrain satisfied the target safety. However, spalling was found in one tooth of the differential pinion gear. The face width of the damaged spiral bevel gear was changed from 41 to 43, and the safety factor was analyzed. The bending and contact safety factors were 1.71 and 1.32, respectively, which were improved by approximately 44% and 18%. It is judged that power transmission would be applied to electric tractors. - COLLAPSE

-
Review Article
- Inertial sensor applications in agriculture: Sensor types and data utilization techniques for mechanical and wearable applications
- Junghwa Park, Seokyung Park, Eunji Jung, Jisu Song, Gunhui Park, Jaehun Lee, Minjoo Kim, Jaesung Park
- Advances in micro-electromechanical systems (MEMS) technology have markedly improved inertial sensors, driving down cost, size, and power consumption while enhancing performance. The …
- Advances in micro-electromechanical systems (MEMS) technology have markedly improved inertial sensors, driving down cost, size, and power consumption while enhancing performance. The resulting growth in supply and demand has created tiered performance classes and price points, enabling broader adoption of inertial sensing in agriculture. In this study, we comprehensively analyzed cases of agricultural application of inertial measurement unit (IMU) or single inertial sensors by classifying them into machine and living objects. In machine targeting research, it has been used as a key element in position estimation and navigation systems for autonomous driving of mobile objects such as agricultural vehicles and robots to detect rapid attitude changes and improve the accuracy of position estimation and path tracking of the mobile object. Cases targeting living objects can be largely divided into livestock and fruit trees. In the case of livestock, wearable IMUs were attached to body parts and combined with various deep learning techniques to detect specific behaviors of livestock or classify behavioral patterns. In the case of fruit trees, a study on vibration harvesting was conducted to analyze the vibration characteristics of fruit trees by attaching acceleration sensors to tree branches or fruits and to optimize vibration parameters. The analysis focused on the types of sensors and data utilization techniques used in each research case, and based on this, we plan to explore ways to utilize IMUs in agriculture in the future. - COLLAPSE
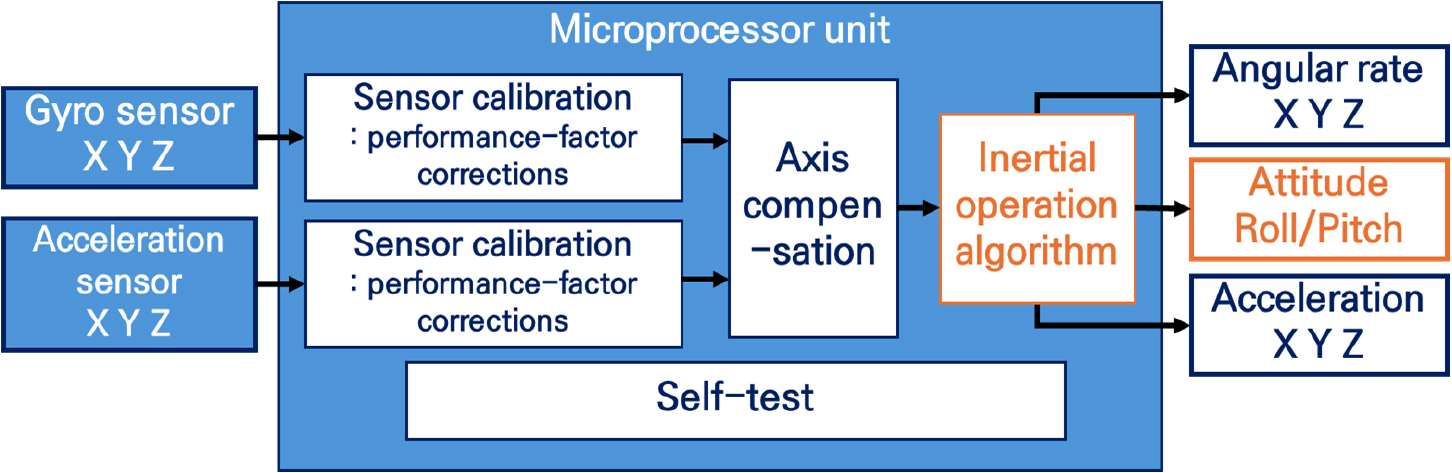
-
Engineering
- Development and verification of a simulation model for the power transmission system of a 20 kW electric tractor
- Dong Wook Kim, Ji Hun Yu, Min Jong Park, Jong Dae Park, Yong Joo Kim
- This study aimed to verify the agricultural working performance of an electric tractor by developing a 1-D power transmission system simulation model …
- This study aimed to verify the agricultural working performance of an electric tractor by developing a 1-D power transmission system simulation model using SimulationX (ver. 4.4, ESI ITI GmbH, Germany). A load measurement system was installed on the electric tractor to measure real-time data during plow tillage, including axle torque and the state of charge (SOC) level of the battery. The t-tests were conducted to compare the measured and simulated axle torques and validated the simulation model. The p-values for the front and rear axles were 0.18 and 0.19, respectively, indicating no statistically significant differences. Although the measured and simulated SOC did not perfectly match, the trends showed similar patterns. The divergences in SOC were mainly due to the resolution limitations of the SOC sensor during measurement. Based on both measured and simulated results, the estimated workable time for plow tillage using the electric tractor was approximately 2 hours. - COLLAPSE
-
Food & Chemistry
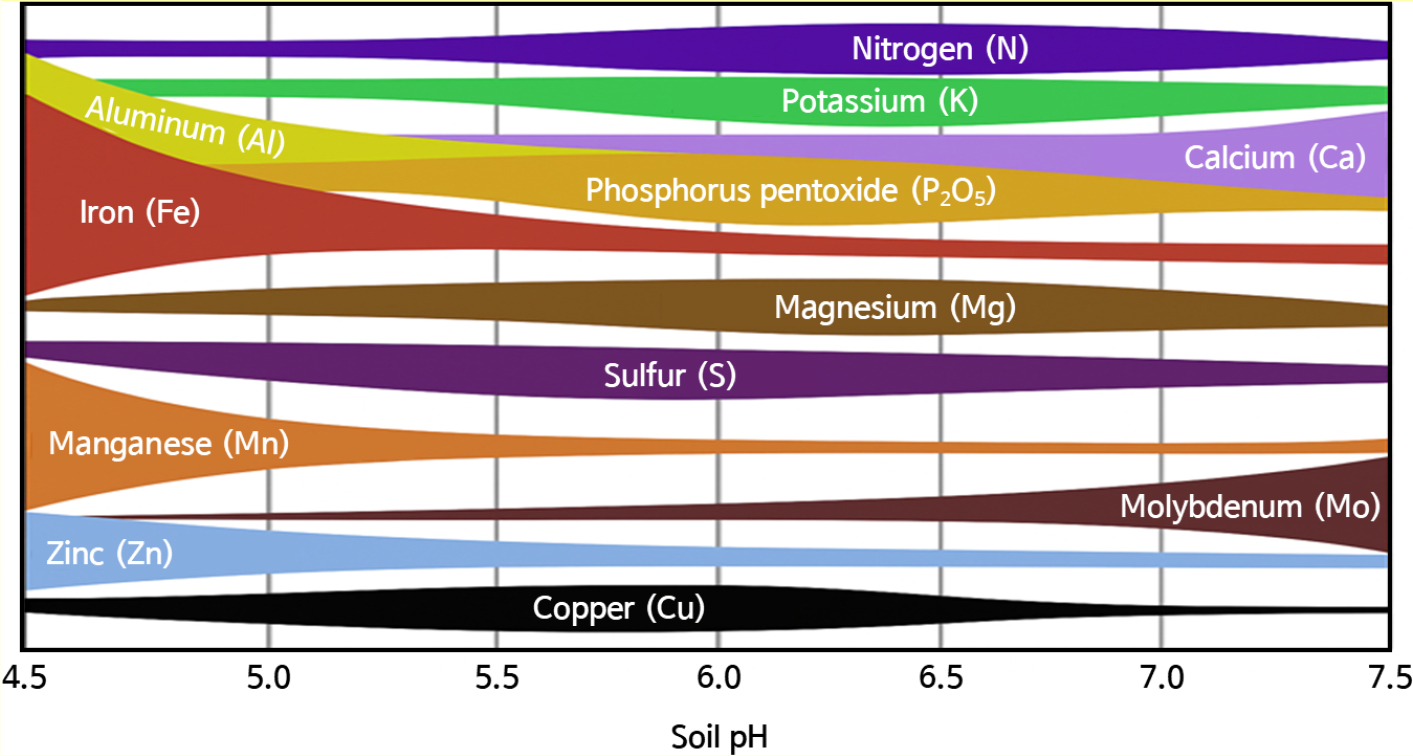
- Short-term effect of biochar application on crop productivity under varying soil pH conditions
- Yun-Gu Kang, Yong-Jun Kim, Jun-Yeong Lee, Jun-Ho Kim, Jiwon Choi, Ji-Hoon Kim, Taek-Keun Oh
- This study evaluated the effects of rice husk biochar (pH 11.0) application on soil properties and Kimchi cabbage (Brassica rapa L. …
- This study evaluated the effects of rice husk biochar (pH 11.0) application on soil properties and Kimchi cabbage (Brassica rapa L. cv. Hwanggeumbaechu) yield under different soil pH conditions. Three soil types, including acidic (pH 3.92), neutral (pH 6.59), and alkaline (pH 8.31), were prepared by adjusting an initial upland soil with 0.1 M hydrochloric acid (HCl) or 0.1 M sodium hydroxide (NaOH), while maintaining other chemical properties constant. Rice husk biochar was applied at 1% (w/w) and compared to an inorganic fertilizer application solely. Biochar application significantly increased soil pH, electrical conductivity (EC), total nitrogen (T-N), organic matter (OM), available phosphorus (Avail. P), and exchangeable Ca2+, with the greatest improvements observed in neutral (pH 6.59) upland soils. Kimchi cabbage showed superior uptake performance of the soil NH4+, NO3−, and Avail. P contents in ranging from pH 6.3 to 6.5, declining under excessive soil alkalinity. Biochar treatment enhanced cabbage yield across all pH conditions, with the highest yield (32.28 Mg·ha-1) in neutral soils, indicating 13% greater than the alkaline counterpart. Nutrient use efficiency (NUE) patterns varied: N and P2O5 uptake decreased with increasing pH beyond neutral, whereas K2O uptake increased under alkaline conditions. These findings indicate that rice husk biochar can improve soil fertility and crop productivity, but its effectiveness depends on initial soil pH. Overly alkaline conditions may reduce the benefits by lowering N and P availability despite improved K uptake. Therefore, soil pH assessment should precede biochar application to maximize agronomic and soil improvement effects. - COLLAPSE
-
Plant & Forest
- Understanding the combined effect of biochar and nitrogen fertilizer on crop yield, nitrogen use efficiency and physiological properties of corn plant
- Rose Nimoh Serwaa, The Ngoc Phuong Nguyen, Taek-Keun Oh, Jwakyung Sung
- Biochar has gained significant attention due to its ability to improve soil quality, reduce carbon emissions and improve crop yield. The use …
- Biochar has gained significant attention due to its ability to improve soil quality, reduce carbon emissions and improve crop yield. The use of only conventional fertilizer is not the way to sustainable agriculture, but the combined use with biochar can improve soil fertility and enhance nutrient uptake. This study used different biochar levels consisting of B0 (0% biochar, 0 g·pot-1); B1 (100% biochar, 4 g·pot-1); B2 (200% biochar, 8 g·pot-1) each combined with nitrogen-based fertilizer (urea and slow releasing fertilizer [SRF]) applied as F1 and F2 respectively under greenhouse environment during the winter season. The data were taken 100 and 121 days after transplanting (DAT). The overall results shows that 200% biochar with urea (B2F1) had a significant influence on plant height, grain dry weight, total chlorophyll, and nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) of about 30%, 200%, 100%, 95% respectively in both Mibaek #2 and Taeyangchal. These findings give a comparable understanding of the physiological growth, grain yield, and enhanced NUE in corn production. - COLLAPSE

-
Engineering
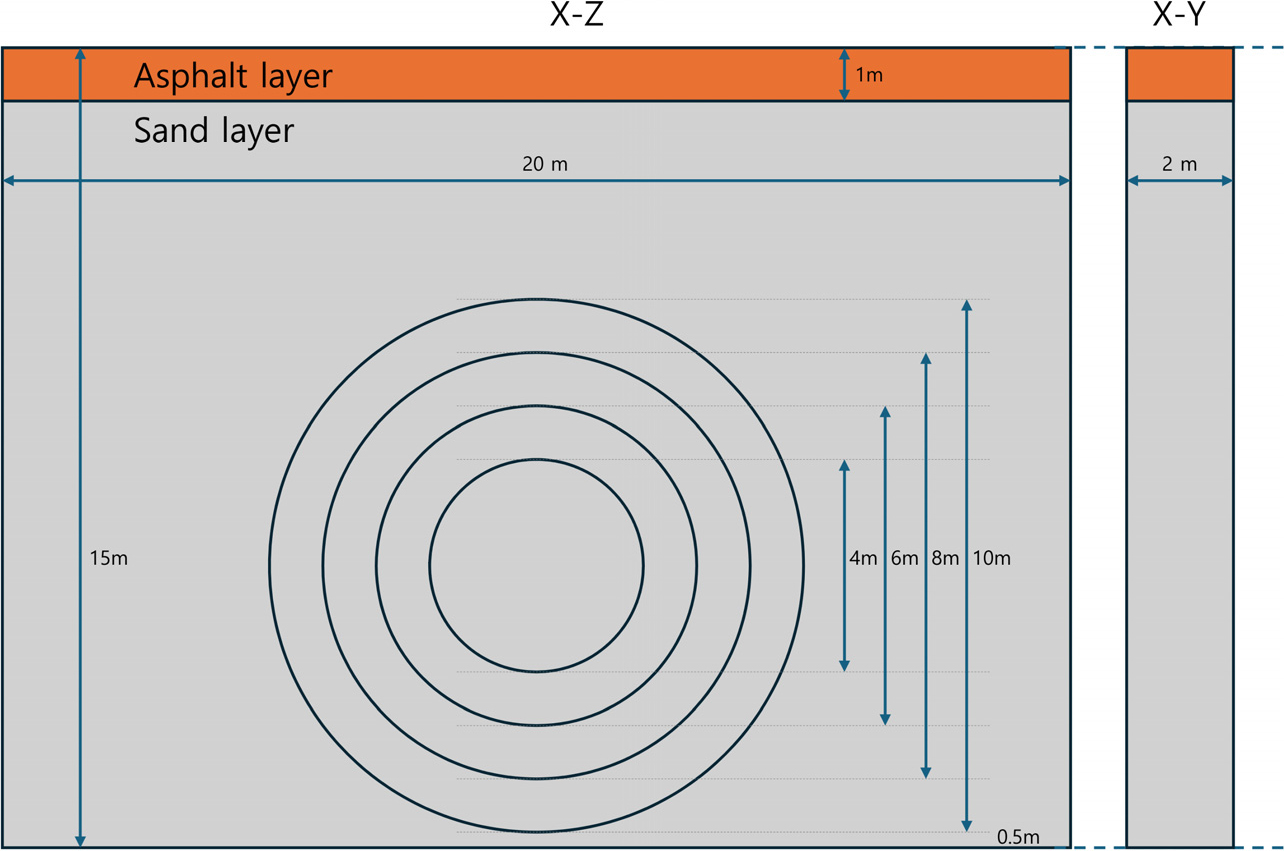
- Numerical investigation of sinkhole behavior and ground collapse induced by subsurface cavity enlargement using the material point method
- Taeun Kang, Seungsoo Lee
- This study numerically investigated sinkhole behavior and ground collapse induced by subsurface cavity enlargement using the material point method (MPM). Four simulation …
- This study numerically investigated sinkhole behavior and ground collapse induced by subsurface cavity enlargement using the material point method (MPM). Four simulation scenarios with varying cavity diameters were designed to analyze the temporal evolution and spatial characteristics of sinkhole initiation and propagation. The results demonstrated that, while larger cavities (Run4, 4 m) exhibited smaller surface subsidence widths compared to smaller cavities, significant vertical deformation and residual voids remained inside the ground. This implied that surface repair alone might not guarantee long-term stability, as additional loading can trigger secondary collapses. The simulation outcomes were consistent with field observations from recent large-scale accidents, such as the 2016 Fukuoka sinkhole in Japan, characterized by sudden extensive collapse, and the 2025 Yashio sinkhole in Saitama Prefecture, where initial localized failure occurred due to sewer pipe corrosion. The findings confirmed that MPM could successfully reproduce both central rapid failure and delayed peripheral collapse patterns, highlighting its utility as a tool for risk assessment and preventive management of urban sinkholes. - COLLAPSE
-
Food & Chemistry
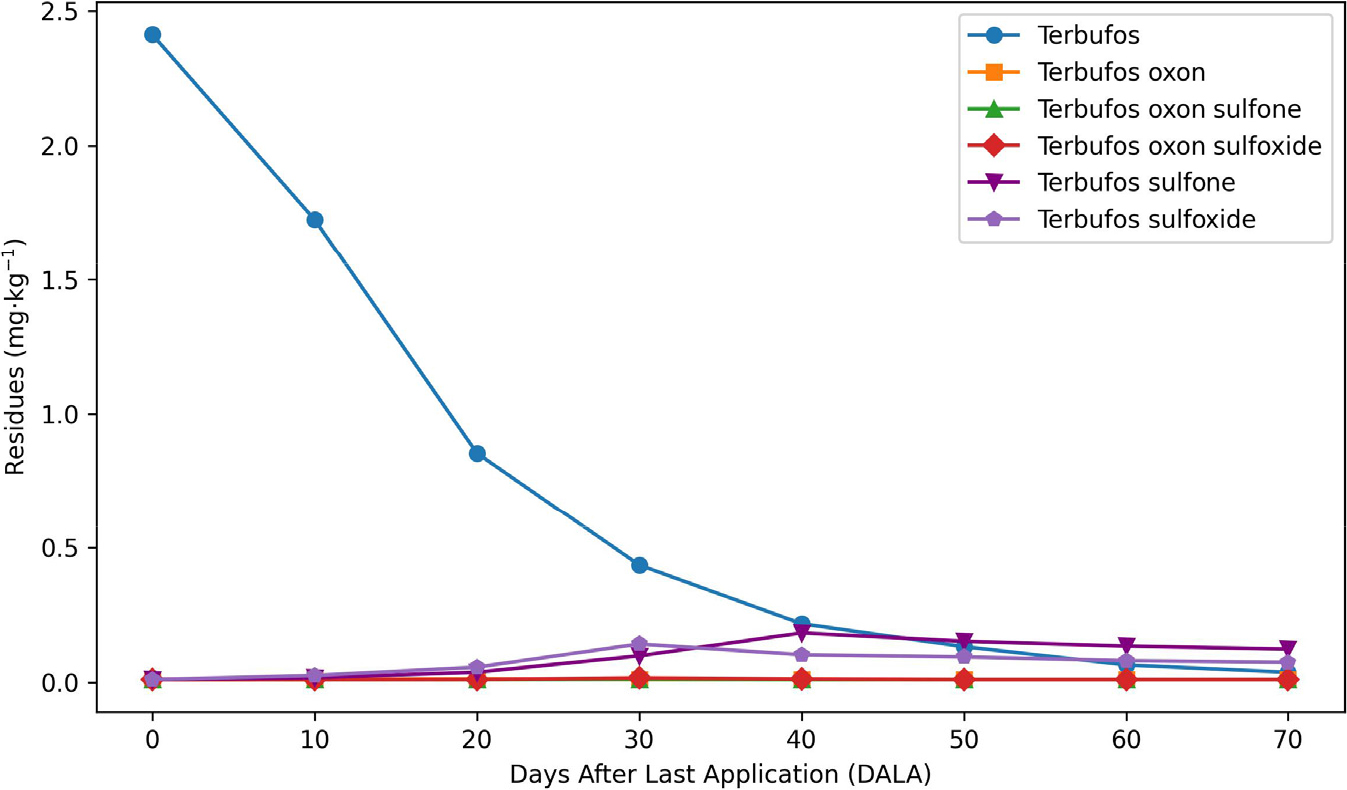
- Residual behaviors of terbufos and its metabolites in preceding and succeeding crops following soil application
- Soon Ho Gwon, Sung Chul Kim
- Terbufos, an organophosphorus insecticide, has been reported to be absorbed by succeeding crops, raising concerns about food safety. This study investigated the …
- Terbufos, an organophosphorus insecticide, has been reported to be absorbed by succeeding crops, raising concerns about food safety. This study investigated the residual behavior of terbufos as an organophosphorus pesticide and its oxidative metabolites, terbufos sulfoxide and terbufos sulfone, in soil and crops. Terbufos (3% granule formulation) was applied to soil at the recommended rate (6 kg·10a-1, hereafter referred to as 1×) and five times the recommended (hereafter referred to as 5×). Two crops, Welsh onion (Allium fistulosum) as the preceding crop and butterbur (Petasites japonicus) as the succeeding crop, were cultivated in the pesticide-applied soil, and residues of terbufos and its oxidative metabolites were analyzed in the harvest of both tested crops. In the recommended dose treatment, the residue levels calculated as the sum of the tebufos-relevant compounds were determined below the maximum residue limit for Welsh onion (0.05 mg·kg-1) and Positive List System (PLS)-requiring detection limit for butterbur (0.01 mg·kg-1). However, residues of terbufos and its oxidative metabolites exceeded the maximum residual limit (MRL) when the pesticide was applied at five times the recommended rate. Time-course soil measurements yielded observed 50% disappearance time (DT50) of approximately 42.5 days for terbufos sulfoxide and 52.3 days for terbufos sulfone in the 1× treatment, and 47.0 days for terbufos sulfoxide and 62.8 days for terbufos sulfone in the 5× treatment. These observed values include formation from the parent compound, and to determine intrinsic metabolite degradation rates, metabolite spike studies or isotope/radiolabel tracing are required. The observed DT50 for terbufos sulfoxide and terbufos sulfone (approximately 42.5 - 62.8 days) reflect both formation from the parent compound and subsequent degradation, and therefore do not represent intrinsic metabolite degradation rates; direct quantitative comparison with the parent compound DT50 (11.6 days for 1× and 12.5 days for 5×) is not warranted. Nonetheless, the temporal profiles indicate that the oxidative metabolites tended to persist longer in soil and reached higher relative abundances in above-ground plant tissues than the parent compound under our experimental conditions, suggesting a potential for metabolite accumulation, particularly at elevated application rates. These findings demonstrate that terbufos is safe under recommended usage, but its oxidative metabolites may accumulate in above-ground crops, highlighting the need for cautious management and monitoring of its residues. - COLLAPSE
-
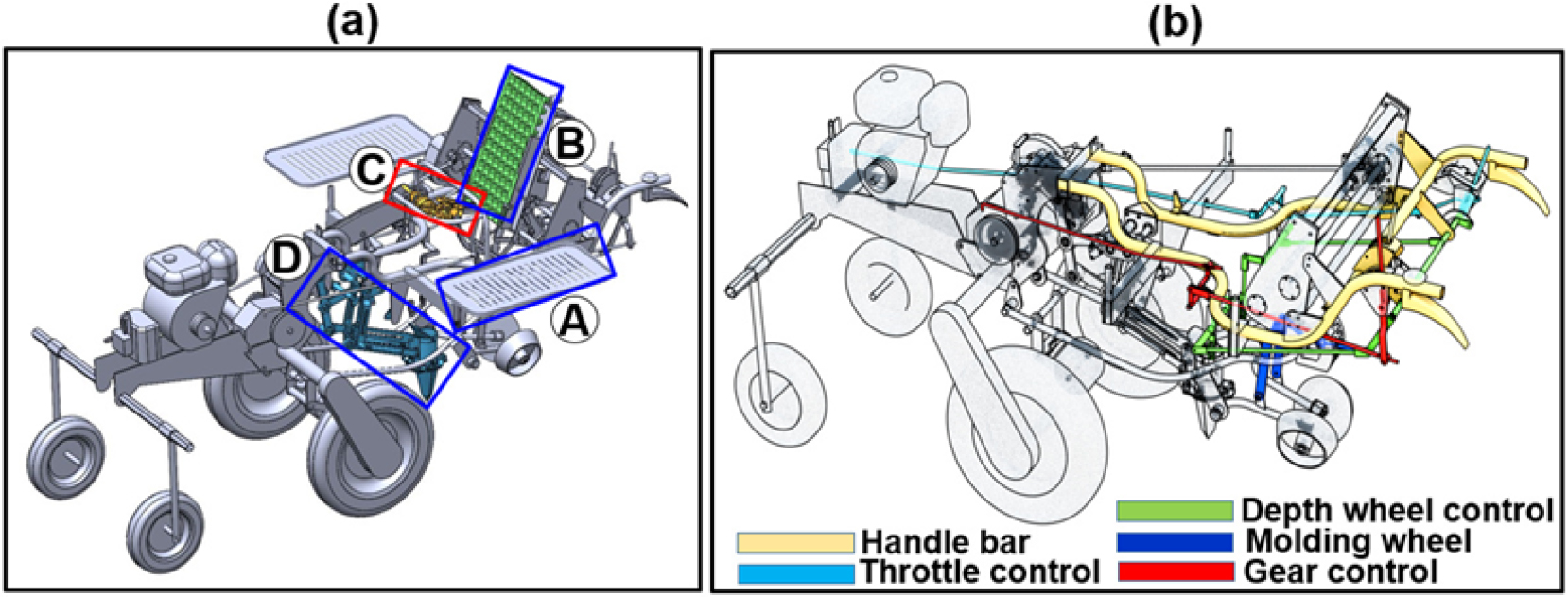
Engineering
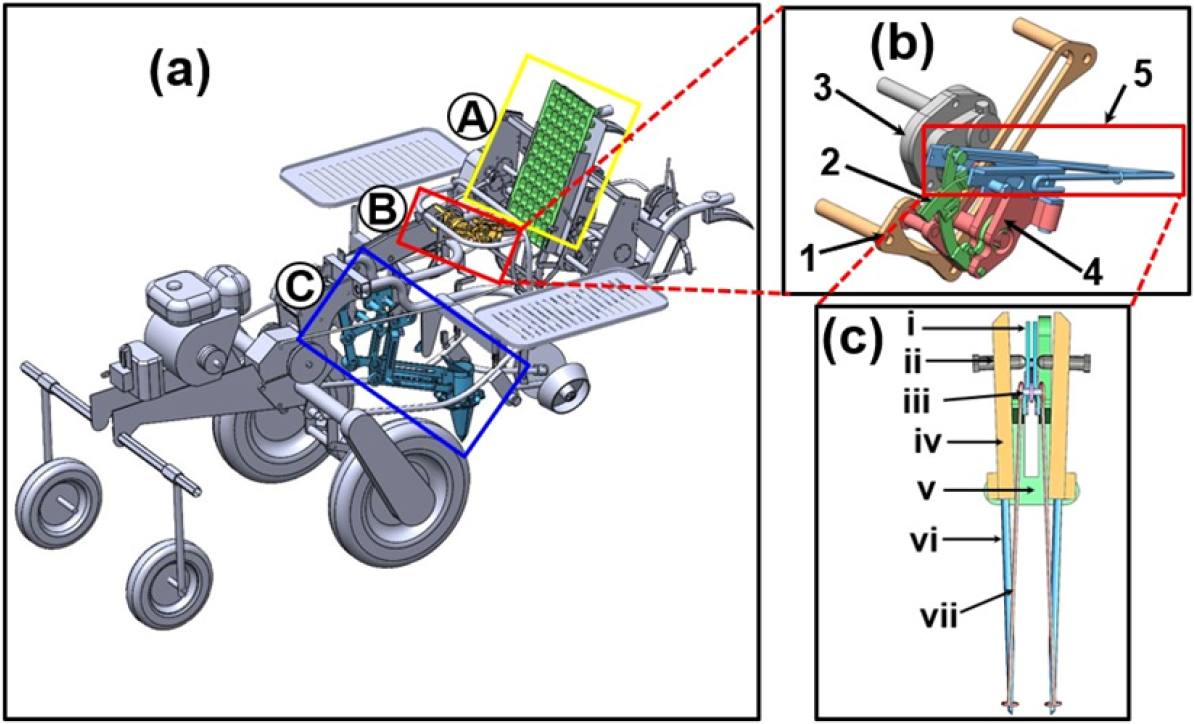
- Kinematic analysis of a gripper-type seedling-picking mechanism for a 3.4-kW walking-type automatic pepper transplanter
- Eliezel Habineza, Md Nasim Reza, Kyu-Ho Lee, Keum-Hee Yang, Seok-Ho Park, Dae-Hyun Lee, Sun-Ok Chung
- Efficient, low-damage seedling transplanting remains a key challenge in vegetable mechanization, particularly amid labor shortages and the growing demand for agricultural productivity. …
- Efficient, low-damage seedling transplanting remains a key challenge in vegetable mechanization, particularly amid labor shortages and the growing demand for agricultural productivity. This study presents the kinematic analysis and field testing of an automatic seedling-picking mechanism for a 3.4-kW walking-type pepper transplanter, with particular emphasis on the motion of the gripper. A gripper-type picking device, consisting of a dual pin, slider, connecting link, fixed slot, and gearbox, was used to extract seedlings from 72-cell nursery trays and transfer them into the planting hopper. A vector-loop model was developed to calculate the position, velocity, and acceleration of the gripper, and a 3D assembly with gripper lengths of 150 - 200 mm, base heights of 15 - 30 mm, and motor speeds of 18 - 36 rpm was used in simulations to identify the optimal configuration. For validation testing, an accelerometer was used to record acceleration data, and for performance testing, the picking device extracted pepper seedlings from a 6 × 12-cell tray placed on a rotary tray conveyor. Selected design consisted of a 160 mm gripper length, a 20 mm base height, and a motor speed of 24 rpm, achieving a smooth seedling-picking trajectory while minimizing mechanical stress and potential damage. Simulated and measured coordinates of the gripper position showed strong agreement, with maximum deviations of 25.76 mm in position, 0.09 m·s-1 in velocity, and 2.53 m·s-2 in acceleration, and the dynamic responses remained within biomechanical safety thresholds. Field validation yielded an average seedling damage rate of 1.73 ± 1.78%, well below the acceptable commercial limit of 5%. These findings confirmed the operational reliability and mechanical compliance of the planting unit, offering a practical solution for efficient and low-damage seedling transplanting in mechanized vegetable production. - COLLAPSE
-
Engineering
- Rollover characteristics of a 3.4-kW walking-type automatic pepper transplanter on sloped conditions
- Eliezel Habineza, Md Nasim Reza, Kyu-Ho Lee, Dae-Hyun Lee, Sun-Ok Chung, Seok-Ho Park
- Rollover accident is a major cause of injury and death in farm machinery, especially on slopes or uneven ground. Enhancing rollover resistance …
- Rollover accident is a major cause of injury and death in farm machinery, especially on slopes or uneven ground. Enhancing rollover resistance and safety is vital for mechanizing labor-intensive crops like pepper, where transplanting is still mostly manual. This study assessed the rollover characteristics of a 3.4 kW walking-type pepper transplanter through simulations and experimental tests under both unloaded and loaded conditions. Rollover metrics including rollover angles, tipping forces, and rollover time were evaluated using multibody dynamics simulation with commercial software and validation tests on an inclination platform. Lateral rollover simulations exhibited consistent angles across load states as 28.20° (left) and 27.90° (right) unloaded, and 27.80° (left) and 27.70° (right) loaded. Measured angles (25.81 - 27.81°) confirmed symmetry and stability in lateral rollover response. The front direction demonstrated the highest stability, with a constant simulated rollover angle of 36.80° and corresponding tipping forces between 1,494 N and 1,518 N. In contrast, the rear direction showed prominent vulnerability, with rollover angles decreasing from 13.50° (unloaded) to 11.20° (loaded), and rollover times as low as 2.12 s. Increased tipping forces in the rear under load further indicate risk associated with rearward center of gravity (CG) shifts. The results offered key insights to improve the stability and safety of walking-type transplanters on sloped fields, particularly by addressing rearward rollover risk and enhancing structural design. - COLLAPSE
-
Plant & Forest
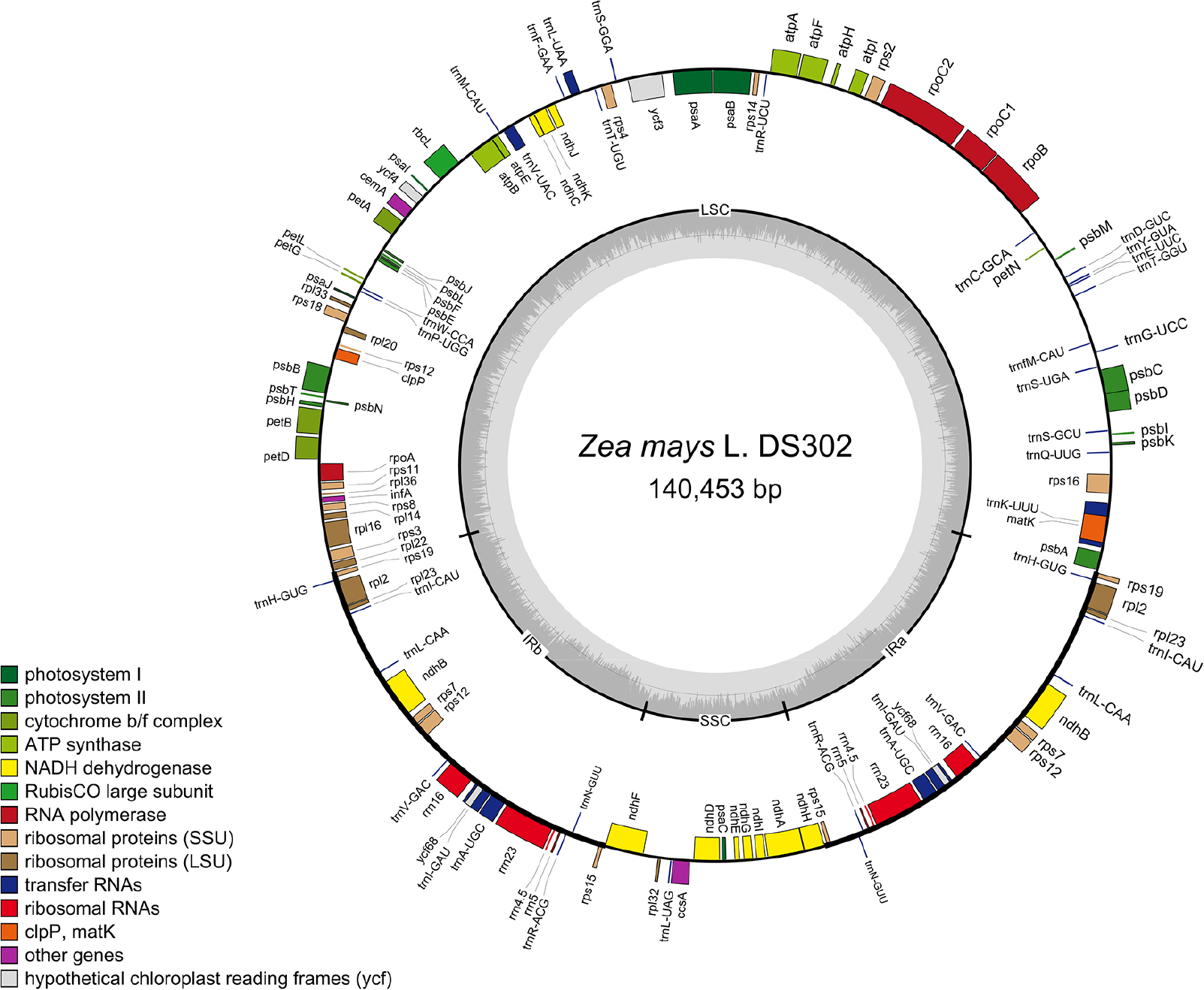
- Chloroplast genome diversity and heteroplasmy in five Korean maize (Zea mays L.) landraces
- Jin Seong Park, Seongmin Hong, Jiyun Go, Myeong-Geon Seok, Hobin Lee, Gibum Yi
- Chloroplast genomes (cpGenomes) provide valuable insights into plant evolution, domestication, local adaptation and genetic diversity. In this study, we sequenced and assembled …
- Chloroplast genomes (cpGenomes) provide valuable insights into plant evolution, domestication, local adaptation and genetic diversity. In this study, we sequenced and assembled the complete cpGenomes of five Korean maize (Zea mays L.) landraces. The assembled cpGenomes ranged from 140,450 to 140,453 bp and exhibited the typical quadripartite structure, comprising large single-copy (LSC), small single-copy (SSC), and inverted repeat (IR) regions. Comparative analysis with the publicly available cpGenomes including B73 revealed high conservation across cpGenome while including several single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and insertions and deletions. Phylogenetic analysis clustered the landrace cpGenomes close to Zhengdan958, reflecting their similar maternal lineages. In addition, variant allele frequency (VAF) analysis revealed varying levels of chloroplast heteroplasmy among landraces, potentially reflecting incomplete sorting of ancestral plastid variants in some accessions. These findings expand the current understanding of cpGenome diversity in maize landraces and provide valuable genomic resources for future studies on maize evolution, adaptation, and breeding. - COLLAPSE
-
Plant & Forest
- Effect of basal fertilizer types and fertigation ratio on yield and nitrogen use efficiency of carrot in upland cultivation
- Minji Kim, Boyun Lee, Minchang Kim, Jwakyung Sung
- As a root vegetable, carrot requires consistent nutrient availability throughout the growing season to reach optimal yield. Developing an effective fertigation strategy …
- As a root vegetable, carrot requires consistent nutrient availability throughout the growing season to reach optimal yield. Developing an effective fertigation strategy is therefore essential for open-field carrot production in upland cultivation. The objective of this study was to investigate nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) and yield under different basal fertilizers (livestock compost, LC; organic fertilizer, OF; and a 1 : 1 mixture, LC+OF) and fertigation ratios (100:0, 50:50 and 30:70). The treatment without fertilizer application was used as the control. The treatments OF100:0, LC30:70, and LC+OF30:70 enhanced nutrient uptake (nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium), NUE, and yield, indicating that synchronizing nutrient release with crop demand is more critical than the absolute basal-to-topdressing ratio. OF supplied readily available N for early growth, while LC supported later uptake through gradual mineralization, underscoring the importance of aligning fertilizer type with fertigation ratio. Further research comparing fertigation with conventional fertilization in upland carrot is needed to confirm these findings across diverse conditions. - COLLAPSE
-
Review Article
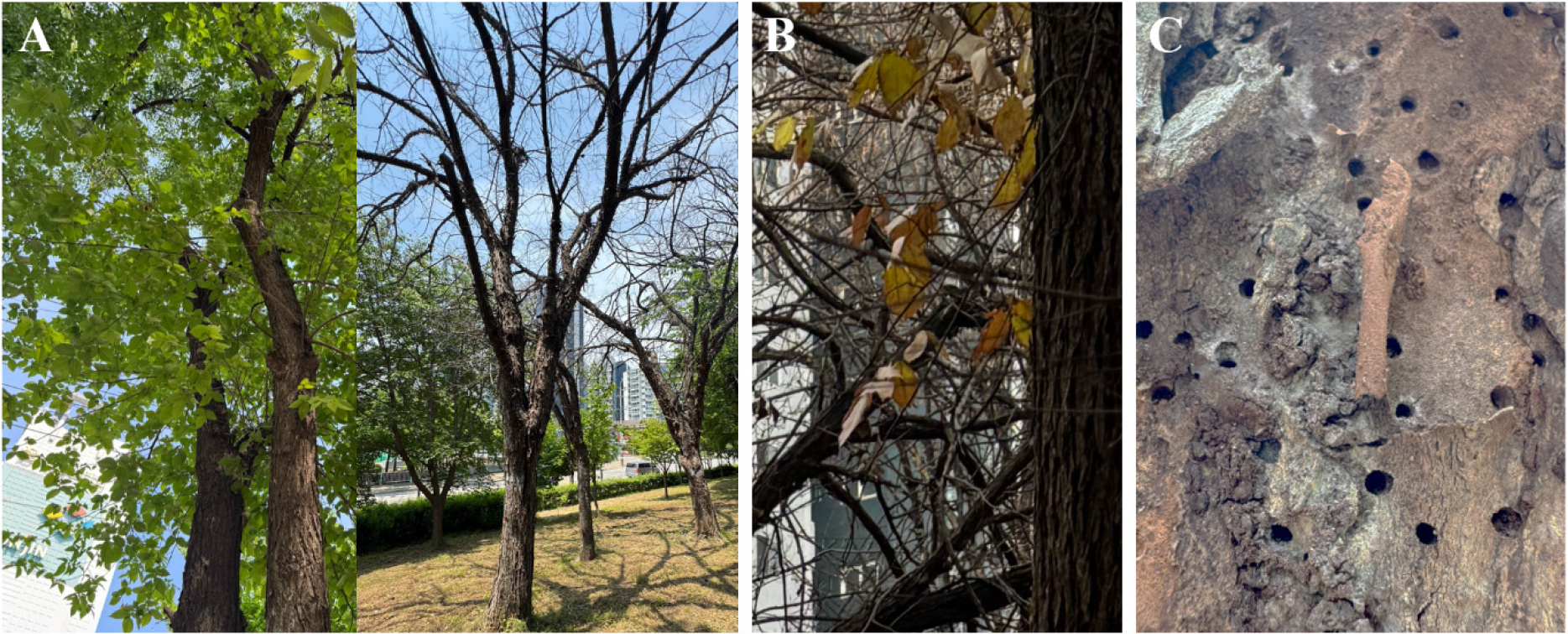
- Review of management strategies on tree diseases caused by emerging and alien pathogens on urban area, with special reference to Dutch elm disease in South Korea: Review of management strategies on tree diseases caused by alien pathogens
- Myeong-Gwan Kim, Hee-Gyu Woo, Yong-Ho Kim, Ki Hyeong Park, Sang-Tae Seo, Bo-Kyung Jang, Dong-Hyeon Lee
- The recent occurrence of Dutch elm disease (DED) in South Korea has highlighted the increasing threat posed by invasive and emerging tree …
- The recent occurrence of Dutch elm disease (DED) in South Korea has highlighted the increasing threat posed by invasive and emerging tree pathogens to both urban and forest ecosystems. In response to these challenges, this review provides a comprehensive synthesis of the occurrence patterns, ecological impacts, and current management policies for high-risk tree diseases in the country, with particular emphasis on exotic and outbreak-prone pathogens. We critically examined the existing national response framework, including legal regulations, institutional roles, and operational protocols, identifying key limitations such as delayed detection, limited availability of registered control agents, and insufficient integration between diagnostic, monitoring, and treatment systems. Policy-level case studies, such as the application of trunk injection technologies for disease control, are discussed not as isolated solutions but as part of a broader integrated management approach. Based on this analysis, we proposed strategic measures to enhance South Korea’s biosecurity capacity, including the establishment of standardized diagnostic pipelines, expansion of pesticide registration for forest pathogens, and strengthening of the Tree Doctor system to enable rapid, science-based responses. By aligning technological innovation with policy development, Korea might improve preparedness and resilience against the accelerating risks of invasive and emergent tree diseases under global trade and climate change pressures. This review aimed to guide policymakers, researchers, and practitioners toward more coordinated and proactive forest health management strategies. - COLLAPSE

-
Management & Economics
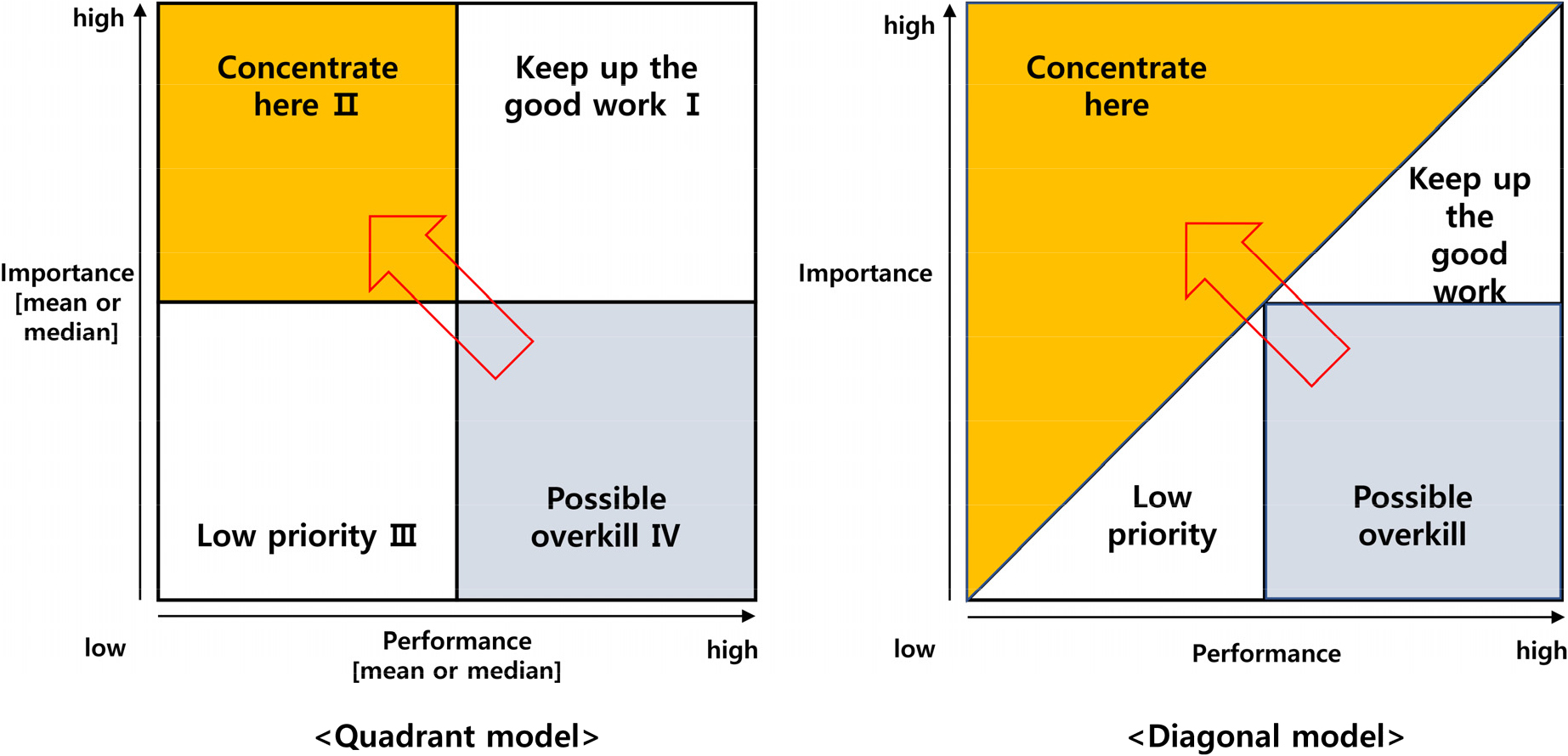
- Analysis of consumer perceptions of food certification
- Gwangsik Oh, Sounghun Kim
- Food products are goods whose quality can only be identified after purchase, which gives them the characteristic of information asymmetry. This makes …
- Food products are goods whose quality can only be identified after purchase, which gives them the characteristic of information asymmetry. This makes it difficult for consumers to purchase what they exactly want. Accordingly, food producers attempt to reduce this asymmetry by providing information on product quality or attributes. However, a problem arises in that consumers cannot fully trust information that is disclosed at the discretion of producers. The Korean government has introduced food labeling certification systems to enhance the credibility of information provided to consumers. While these systems offer diverse information on food quality, safety, and differentiated attributes, they have been criticized for insufficiently reflecting consumer needs. Moreover, the government administers certification from a supplier-oriented perspective, similar to producers, thereby failing to deliver the information most relevant to consumers. The purpose of this study is to analyze consumer perceptions of food labeling certification and to derive implications for improving the system. Specifically, it examines the results of a consumer survey and explores possible improvements to the food labeling certification system through importance-performance analysis (IPA). The analysis yielded the following implications. First, Korean consumers demonstrate relatively high awareness and utilization of food labeling certification. Second, consumers expressed positive attitudes toward the introduction of privately-led food certification labeling systems, suggesting the need to integrate existing certifications and to incorporate new information such as producers’ fulfillment of social values. Third, while policies on food labeling certification are generally appropriate, improvements are required in detailed standards, promotional strategies, and the credibility of the institutions responsible for managing the system. - COLLAPSE
-
Animal
- Effects of reed mixing ratios in cow manure on the chemical composition and heavy metal content of earthworm castings
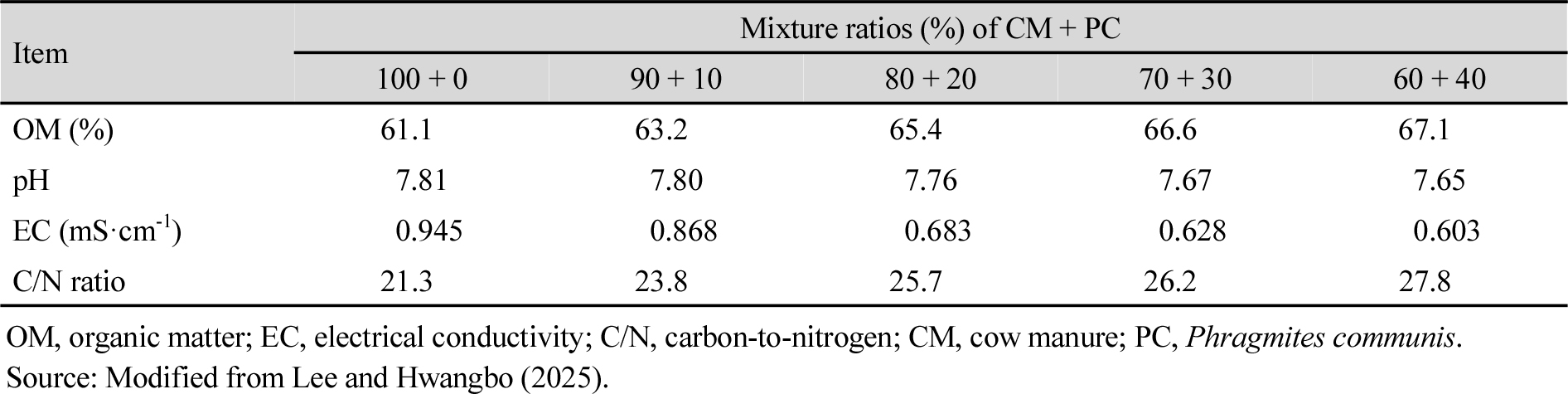
- Soon Hwangbo, Ji-Hong Lee
- This study aimed to determine the effects of different mixing ratios of reed (Phragmites communis) with cow manure on the …
- This study aimed to determine the effects of different mixing ratios of reed (Phragmites communis) with cow manure on the chemical properties and heavy metal concentrations of earthworm (Eisenia foetida) castings, in order to establish optimal vermicomposting conditions for sustainable agriculture and environmental protection. The earthworm castings used in this work came from an earlier test where cow manure and reed were mixed in different volume ratios (100 : 0, 90 : 10, 80 : 20, 70 : 30, and 60 : 40) and given to E. foetida for 70 days. Chemical analyses included organic matter (OM), pH, electrical conductivity (EC), total carbon (TC), total nitrogen (TN), and the carbon-to-nitrogen (C/N) ratio. Heavy metals such as arsenic (As), cadmium (Cd), chromium (Cr), copper (Cu), and lead (Pb) were measured by atomic absorption spectrophotometer (AAS) or inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry (ICP-AES) method, while mercury (Hg) was not found in the samples. The OM content of the castings (51.60 - 57.63%) was lower than that of the feed (61.10 - 67.10%), but it showed a significant increase as the mixing ratio of reed increased (p < 0.05). Casting pH (6.77 - 7.25) and EC (0.576 - 0.830 mS·cm-1) were lower than in feed and decreased significantly as reed proportions increased (p < 0.05). TC increased from 28.67% in pure manure to 32.01% at 40% reed, while TN peaked in pure manure (1.58%) and at 10% reed (1.55%). The C/N ratio in castings (18.11 - 22.84) was lower than in feed but increased with reed addition. The heavy metal content in the castings was 19 - 25% lower than that in the feed. Levels of As, Cd, Cr, Cu, and Pb all showed a significant decrease as the proportion of reed increased (p < 0.05). When the reed portion in cow manure increased during vermicomposting, OM and TC showed higher values, while pH, EC, and heavy metal contents became lower in the castings. These findings indicate that higher reed ratios can enhance the agronomic quality and environmental safety of earthworm castings for use as organic fertilizers and soil amendments. - COLLAPSE
-
Review Article
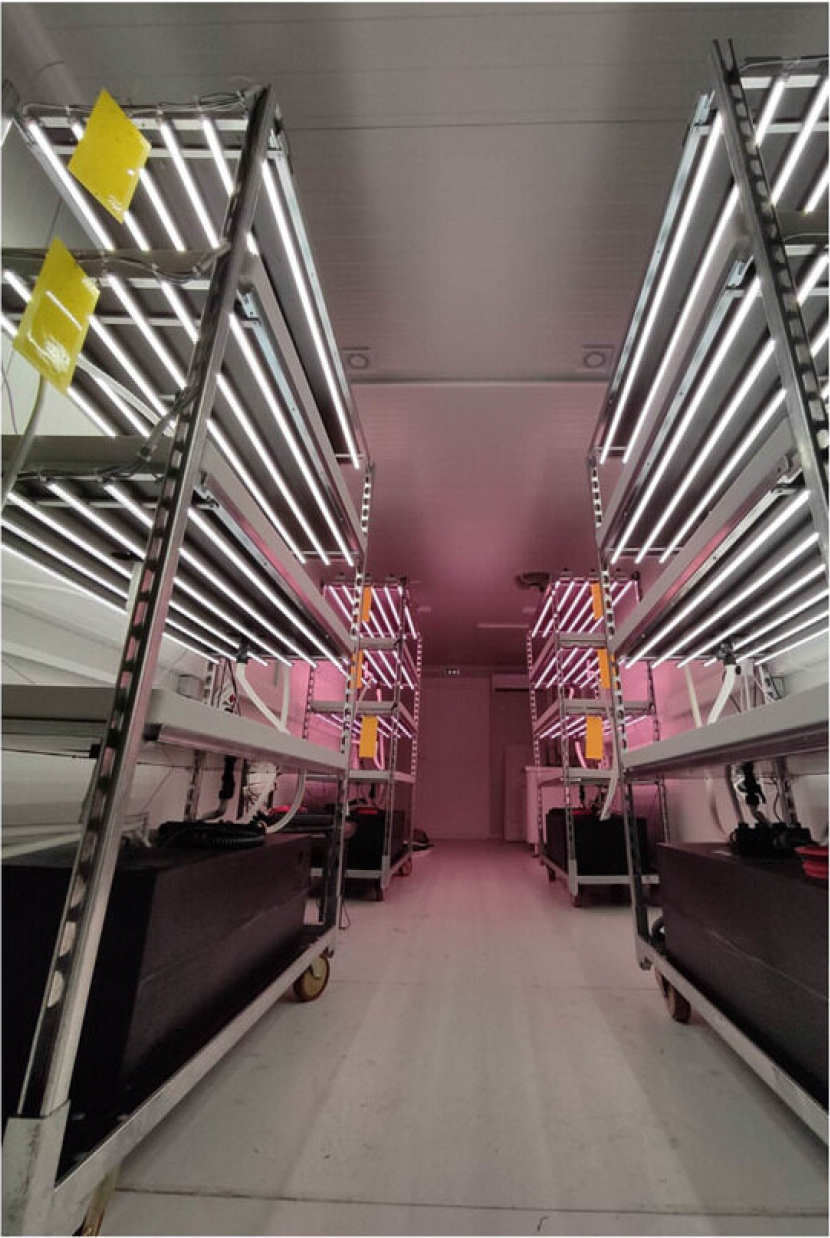
- Advancements in vertical farming: A review of potentials, challenges, and prospects
- Timothy Denen Akpenpuun, Hamidu Oladimeji Sanusi, Oluwasegun Moses Ogundele, Abdulgafar Usman, Azuatalam Reginald Gbenga, Qazeem Opeyemi Ogunlowo
- Vertical farming or vertical growing systems, a subset of controlled environment agriculture (CEA), integrates smart and precision agriculture to optimize crop production …
- Vertical farming or vertical growing systems, a subset of controlled environment agriculture (CEA), integrates smart and precision agriculture to optimize crop production in stacked environments within a greenhouse, utilizing Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, automation, and advanced lighting. However, vertical farming can be carried out in the open, but the advantages of a closed system are sacrificed. This review examines recent advancements, including precision irrigation (hydroponics, aeroponics, and aquaponics), LED spectral optimization, robotics, and machine learning (ML) for enhanced resource efficiency. Case studies from Singapore, Japan, and the Netherlands demonstrate yield increases of 200 - 300% and energy savings of 30 - 50% compared to traditional methods. By integrating robotics, ML, and IoT, yields can be maximized, resource utilization can be optimized, and environmental impact can be reduced. Case studies from Singapore, Japan, and the Netherlands demonstrate the potential, with kale yields of 300 t·ha-1, strawberry production at 200 t·ha-1, and dual basil fish outputs achieved through 98% water recycling. Challenges such as high costs, energy demands, and technical complexity persist, particularly in developing regions. Future directions propose the integration of renewable energy, can offset energy reliance, cutting costs by 50%, low-cost sensors that broaden access and simplify IoT deployment, and modular designs that enhance scalability and offer hope for adaptation. This manuscript synthesizes quantitative metrics, comparative analyses, and implementation challenges, providing engineers and researchers with a detailed framework to advance sustainable urban agriculture through technology-driven solutions. - COLLAPSE

-
Plant & Forest
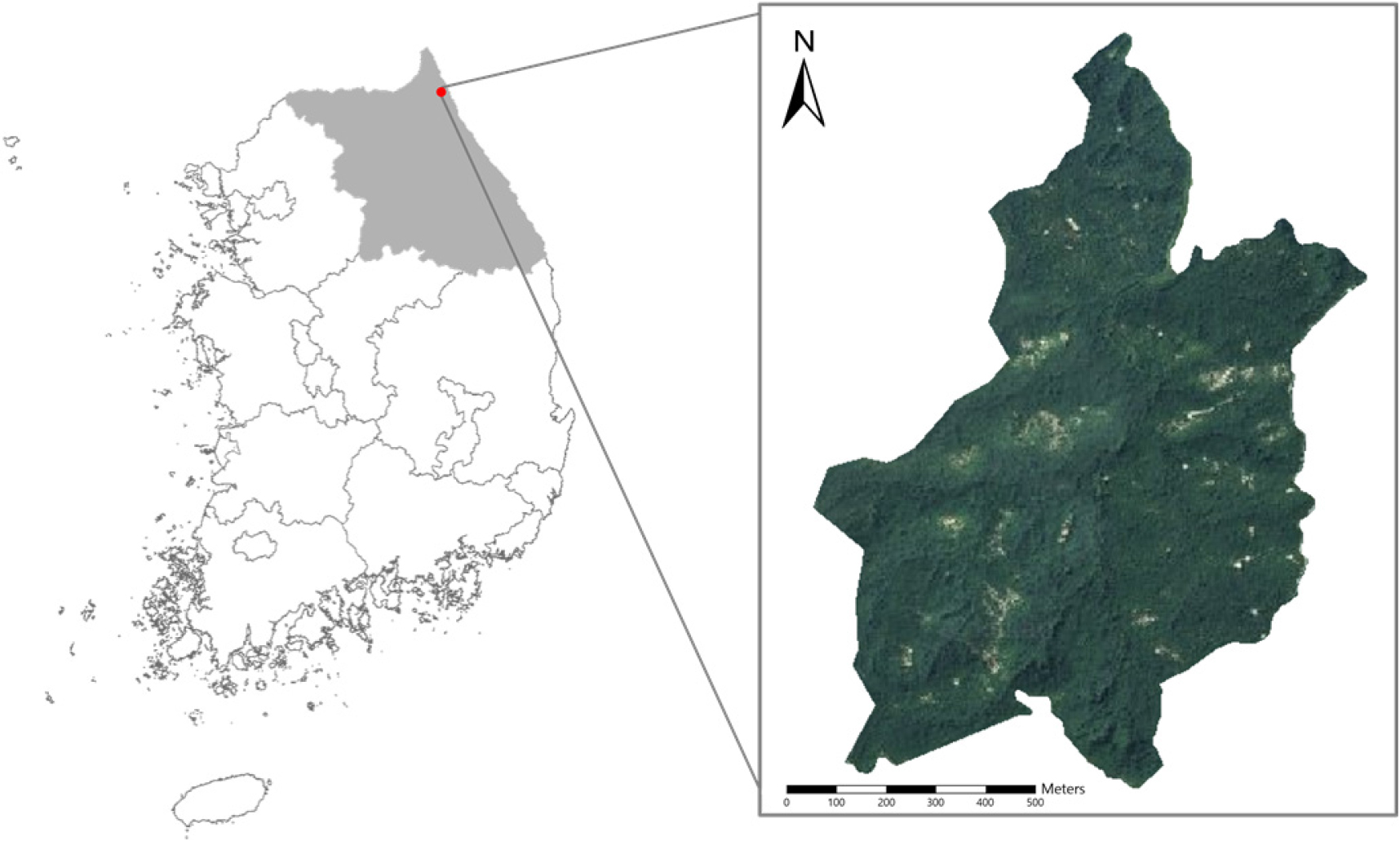
- Application of LANDIS-II for analyzing post-fire forest succession in Korea
- Jinsol Lim, Jae-Yong Choi
- Wildfire is a major disturbance that fundamentally alters forest ecosystem structure and function. This study applied the LANDIS-II forest landscape model with …
- Wildfire is a major disturbance that fundamentally alters forest ecosystem structure and function. This study applied the LANDIS-II forest landscape model with the PnET-Succession module to simulate 25 years (2000 - 2025) of post-fire forest succession in a natural restoration site affected by the 2000 East Coast wildfire in Goseong, South Korea. Model inputs included ecoregion maps, initial community data, climate records, and species parameters calibrated using domestic and international references. Simulation results predicted Quercus mongolica dominance across 63.8% of the area, followed by Pinus densiflora (32.4%) and Quercus variabilis (3.8%). Field surveys in 2025 showed similar patterns with Q. mongolica dominating 73.7% of surveyed sites, confirming a clear transition from coniferous to deciduous forests. However, P. densiflora distribution was limited to peripheral areas in field observations, contrasting with model predictions. This discrepancy was attributed to two main factors: (1) incomplete parameter calibration, with only 6 of 28 physiological parameters adjusted using local data, and (2) the small spatial scale (82 ha) relative to LANDIS-II’s recommended application scale (> 10,000 ha), which limits the representation of edge effects and seed dispersal. These results highlight both the potential and limitations of LANDIS-II for Korean forest applications, emphasizing the necessity of localized parameter calibration and finer-scale input data. The study provides a quantitative foundation for predictive modeling of post-fire restoration and adaptive forest management under climate change. - COLLAPSE
-
Animal
- Effects of Isulsongi mushroom (Lentinula edodes GNA01) supplementation on age-dependent blood lipid characteristics in dogs
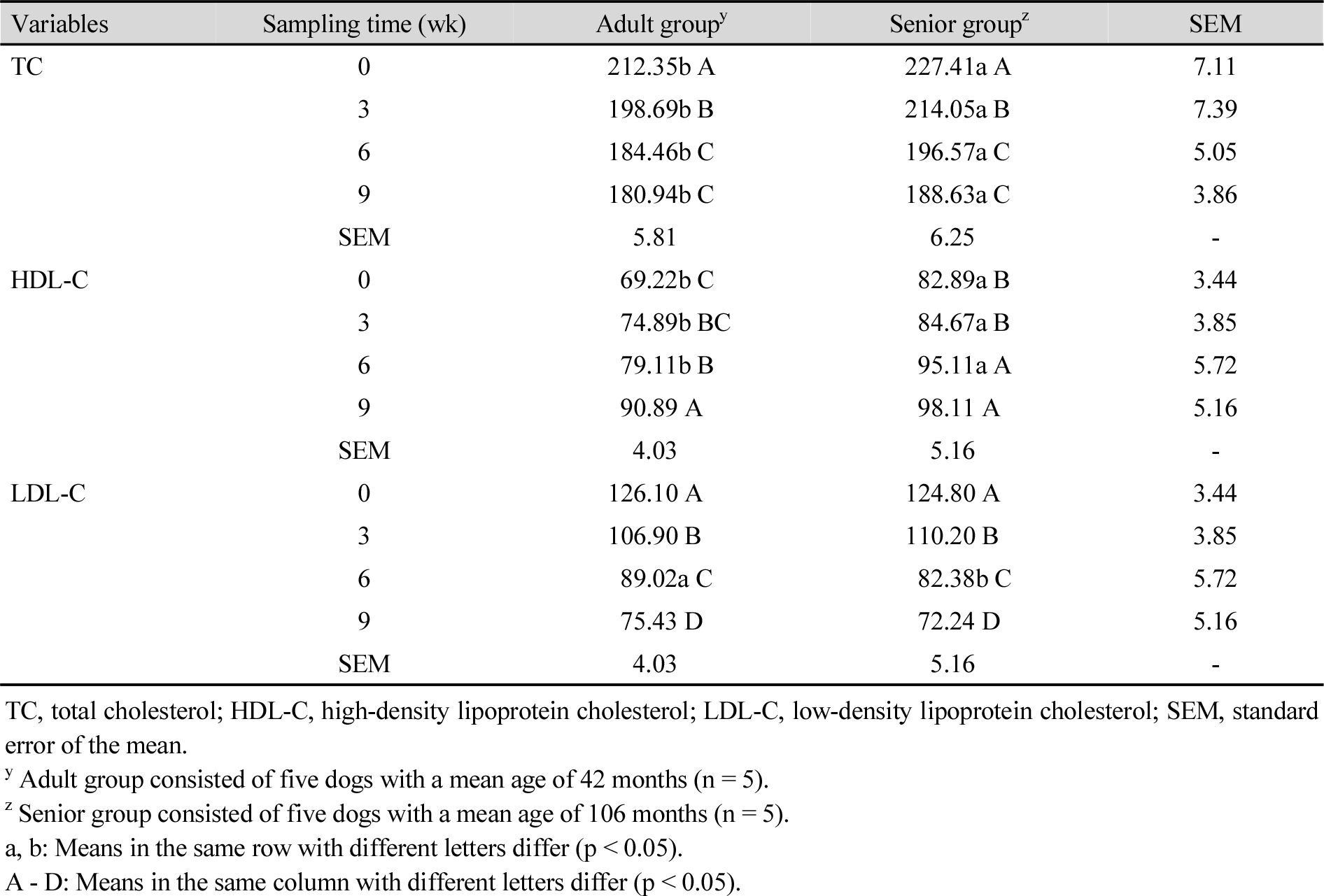
- Eun-Gyeom Jung, Soon Hwangbo
- This study examined the effect of feeding Isulsongi mushroom (Lentinula edodes GNA01), a new cultivar of shiitake, on blood lipid traits …
- This study examined the effect of feeding Isulsongi mushroom (Lentinula edodes GNA01), a new cultivar of shiitake, on blood lipid traits in dogs of different ages. Ten Maltese dogs were divided into two groups, adult (average 42 months) and senior (average 106 months), and fed freeze-dried mushroom powder at 150 mg·kg-1 body weight daily for 9 weeks. Blood samples were taken at 0, 3, 6, and 9 weeks and analyzed for total cholesterol (TC), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), triglycerides (TGs), atherogenic index (AI), and cardiac risk factor (CRF). Results showed TC and LDL-C decreased significantly in both groups, while HDL-C increased. TGs decreased significantly in adults, whereas in seniors the decline was not statistically significant. AI and CRF values also dropped in both age groups as feeding period continued. Senior dogs tended to have higher lipid values overall; however, they still showed a response to supplementation. These findings suggest Isulsongi mushroom can improve lipid metabolism and reduce cardiovascular risk markers in dogs, although the strength of the effect may differ depending on age. The results may be useful for developing functional pet food materials and age-specific nutrition strategies. - COLLAPSE
-
Animal
- Effects of dietary crude protein levels with lysine supplementation on growth performance, meat quality, nitrogen excretion, and hematological parameters in finishing pigs
- Su Hyun An, Hwan-Ku Kang, Jin Young Jeong, Min Ji Kim, Pil-Nam Seong, Dong-Gyun Kim, Seong-Hun Shim
- This study aimed to evaluate the effects of reducing dietary crude protein (CP) by 1%-unit and supplementing with three graded levels of …
- This study aimed to evaluate the effects of reducing dietary crude protein (CP) by 1%-unit and supplementing with three graded levels of lysine (Lys) on growth performance, carcass characteristics, meat quality, nitrogen utilization, and blood parameters in finishing pigs. Four dietary treatments were used, consisting of a control diet containing 14% CP and 0.91% Lys and three different diets containing 13% CP with graded Lys levels of 0.91, 0.98, and 1.06%, respectively. Two experiments were conducted using the same dietary treatments. In the feeding trial, 48 pigs (initial body weight [BW]: 85 ± 5 kg) were assigned to four treatments in a 35-day trial (3 pigs/pen). In the metabolic trial, 12 pigs were allocated to four metabolic cages (3 pigs/treatment) for a 7-days trial. In the feeding trial, reducing dietary CP improved gain-to-feed ratio (p < 0.001), with the best results observed in pigs fed 13% CP diets containing 0.98% and 1.06% Lys. However, dressing rate decreased as dietary Lys concentration increased (p = 0.011). In the metabolic trial, weight gain improved linearly with increasing dietary Lys (p = 0.044). Meanwhile, reducing dietary CP by 1%-unit significantly decreased retained nitrogen (p = 0.038) and absorbed nitrogen (p = 0.005). The blood glucose concentration increased linearly (p = 0.018) as dietary Lys concentration increased, whereas the number of neutrophils showed a quadratic increase in response to dietary Lys levels (p = 0.029). These findings suggest that reducing dietary CP by 1%-unit, when accompanied by appropriate Lys supplementation, can maintain or even improve growth performance and nitrogen utilization in finishing pigs without negatively affecting carcass weight and meat quality. - COLLAPSE

-
Plant & Forest
- Screening and selection of strawberries resistant to Fusarium wilt using cultivars and breeding populations
- Min-Young Kim, Do Yoon Lim, Suho Lee, SeoWoo Beak, Marc Semunyana, Soomin Lee, Bomee Lee, Hyun-ju Kim, Jun Namgung, Eun-kyu Choi, KyuJeong Lim, Gil-joon Choi, Ji-Eun Lee, Je Hyeok Yoo, Han Na Park, Inha Lee, Sun Ha Kim, Jiyoung Min, Sang-Keun Oh
- Strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa) is one of the most economically important horticultural crops in Korea, accounting for the largest share …
- Strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa) is one of the most economically important horticultural crops in Korea, accounting for the largest share of vegetable production with an estimated market value of approximately KRW 1.5 trillion. In recent years, fresh strawberries have become a major export commodity, particularly to Southeast Asian markets such as Hong Kong, Singapore, and Thailand. However, most newly developed cultivars following ‘Seolhyang’—including ‘Maehyang’, ‘Kingsberry’, and ‘Highberry’—while exhibiting superior fruit quality and consumer appeal, remain highly susceptible to soil-borne diseases, posing challenges to stable cultivation. Among these, strawberry wilt caused by Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. fragariae is a major constraint to sustainable production, as the pathogen invades the vascular system, leading to wilting and plant death, and can cause yield losses of up to 30% under warm and humid conditions intensified by climate change. In this study, 93 strawberry lines, including domestic and international cultivars and breeding populations, were evaluated for resistance to Fusarium wilt. Disease severity was assessed for four weeks after inoculation on a 0 - 5 scale based on symptom progression. A wide range of variation in disease response was observed: 37 resistant (R) lines (0.0 - 0.9), 39 moderately resistant (MR) lines (0.98 - 2.08), 12 susceptible (S) lines (2.24 - 3.25), and 5 severely susceptible (SS) lines (3.75 - 4.49). The identification of highly resistant lines provides valuable genetic resources for the development of new Fusarium wilt-resistant strawberry cultivars with enhanced horticultural performance and field adaptability. - COLLAPSE

-
Management & Economics
- Household meat demand with consumer expenditure survey data
- Jun Man Jang, Songhyun Hong, Jae Bong Chang
- Economic growth and rising incomes have significantly increased protein intake through meat consumption. This trend, combined with the rapid Westernization of diets …
- Economic growth and rising incomes have significantly increased protein intake through meat consumption. This trend, combined with the rapid Westernization of diets and increased consumption of processed foods and dining out, has led to per capita meat consumption surpassing rice consumption in Korea. Understanding the dynamics of meat demand is critical, especially given that demographics are expected to further impact consumption patterns. This study analyzes the meat demand system by focusing on the estimation of own-price and cross-price elasticities and, specifically, the effect of changes in household size. We employ the Quadratic Almost Ideal Demand System (QUAIDS) model using consumer expenditure survey data for fresh meat products. Our findings reveal that consumer demand for both domestic and imported beef is own-price elastic, while demand for domestic pork is own-price inelastic. Generally, a substitution relationship exists among meats consumed domestically. However, results suggest that the substitutability is lower than conventionally assumed because domestic and imported beef are perceived as distinct goods due to quality and price differences. Furthermore, the consumer response (substitution effect) remains relatively insensitive to price changes between domestic pork and imported beef/pork. All meats demonstrate positive expenditure elasticity, with beef higher than pork. One- and two-person households were found to exhibit the largest own-price elasticity and the smallest expenditure elasticity for domestic beef and pork. As these smaller households grow, continuous policy attention is needed to sustain domestic meat consumption. - COLLAPSE
-
Engineering
- Performance and economic analysis of onion harvesters: A comparison of tractor-mounted digger–collector combination and self-propelled integrated harvester
- Jae-Seo Hwang, Seung-Min Baek, Seung-Yun Baek, Yong-Joo Kim, Wan-Soo Kim
- Mechanization rate of onion harvesting remains low due to labor shortages and high costs. Efficient and economical mechanization strategies should be explored. …
- Mechanization rate of onion harvesting remains low due to labor shortages and high costs. Efficient and economical mechanization strategies should be explored. This study compared performance and economic feasibility of a tractor-mounted digger–collector (Scenario 1) and a self-propelled harvester (Scenario 2). Performance was evaluated by work efficiency, loss, damage, and foreign-matter rates, while economic analysis classified costs into unit-area cost and total cost according to machine operating period and cultivated area. Scenario 2 outperformed Scenario 1, with a field capacity of 0.094 ha·h-1, a loss rate of 0.58%, and a damage rate of 4.52%, compared with 0.067 ha·h-1, 5.44%, and 22.9% for Scenario 1. However, the foreign matter rate of Scenario 2 (4.50%) was higher than that of Scenario 1 (1.24%). In the economic analysis, Scenario 2 reduced unit-area costs by up to 69.5% owing to the lower initial investment, higher operational efficiency, and reduced losses. Moreover, even as the machine operating period and cultivated area increased, Scenario 2 maintained lower costs with a smaller rate of increase. In conclusion, the self-propelled harvester exhibited greater potential for field application than the separate system in terms of operational efficiency and economic feasibility. However, the curing process, which may affect storability, was not considered and should be addressed in future studies. - COLLAPSE
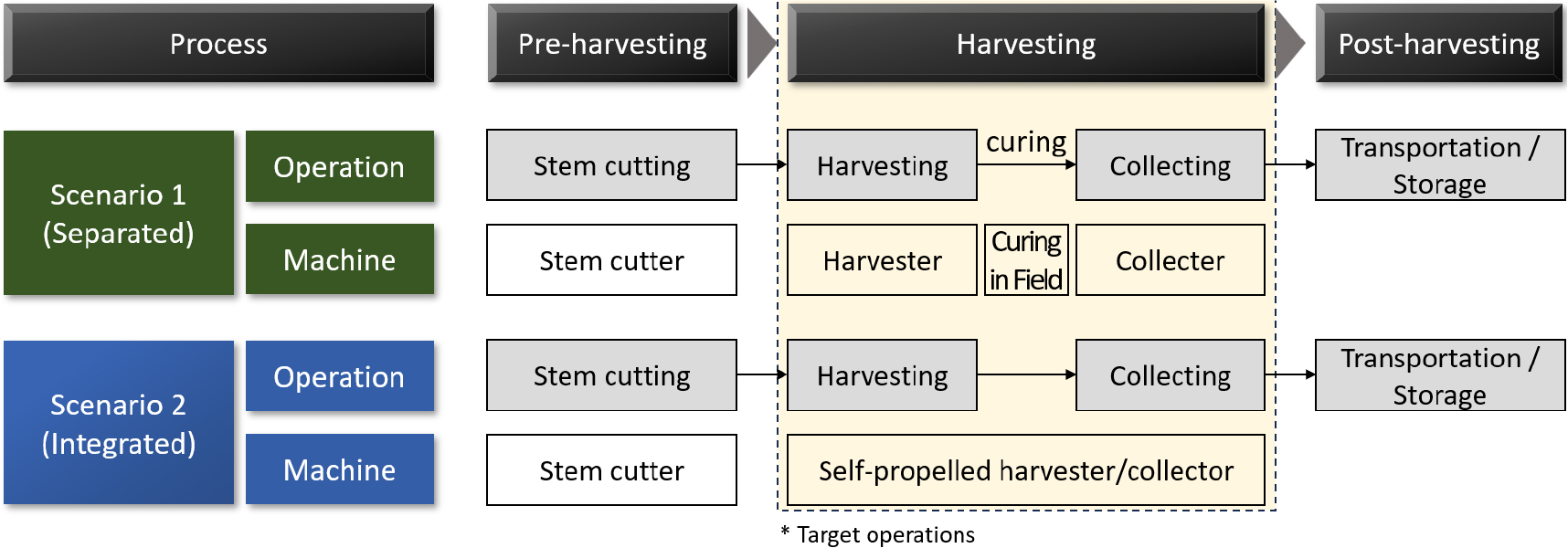
-
Engineering
- Measurement of physical and contact properties of garlic bulbs for computational modeling
- Jae-Seo Hwang, Si-Eon Lee, Young-Woo Do, So-Yun Gong, Hyeon-Seo Yoon, Seon-Ju Park, Gi-Deok Kim, Seung-Gwi Kwon, Seok-Pyo Moon, Seung-Yun Baek, Wan-Soo Kim
- Aim of this study was to measure the physical and interaction parameters between garlic bulbs and contact materials for use in discrete …
- Aim of this study was to measure the physical and interaction parameters between garlic bulbs and contact materials for use in discrete element method (DEM) simulations. Garlic bulbs were classified into three size groups—small, medium, and large—and their geometric dimensions (width and height), weight, water content, coefficient of static friction, and coefficient of restitution were measured. These parameter values were obtained using standard measurement tools and established test methods. As the size category increased, the bulbs showed a clear increasing trend in width (4.29 - 5.88 cm), height (3.12 - 3.78 cm), and weight (39.1 - 73.0 g). Experimental results showed that the static friction coefficient increased with bulb size, ranging from 0.3806 - 0.4499 for metal, 0.5834 - 0.6043 for soil, and 0.5427 - 0.6215 for rubber. In contrast, the coefficient of restitution decreased with increasing bulb size, with values ranging from 0.3646 - 0.3979 for metal, 0.2079 - 0.2514 for soil, and 0.2951 - 0.3699 for rubber, while no distinct trend was observed for garlic–garlic collisions (0.8668 - 0.8869). These findings indicated that both material type and bulb size significantly influenced contact behavior, highlighting the need for precise, condition-specific parameter inputs for accurate DEM simulations. The parameters and their trends derived from this study are expected to serve as fundamental reference data for future DEM-based analyses of garlic–machine interactions. - COLLAPSE
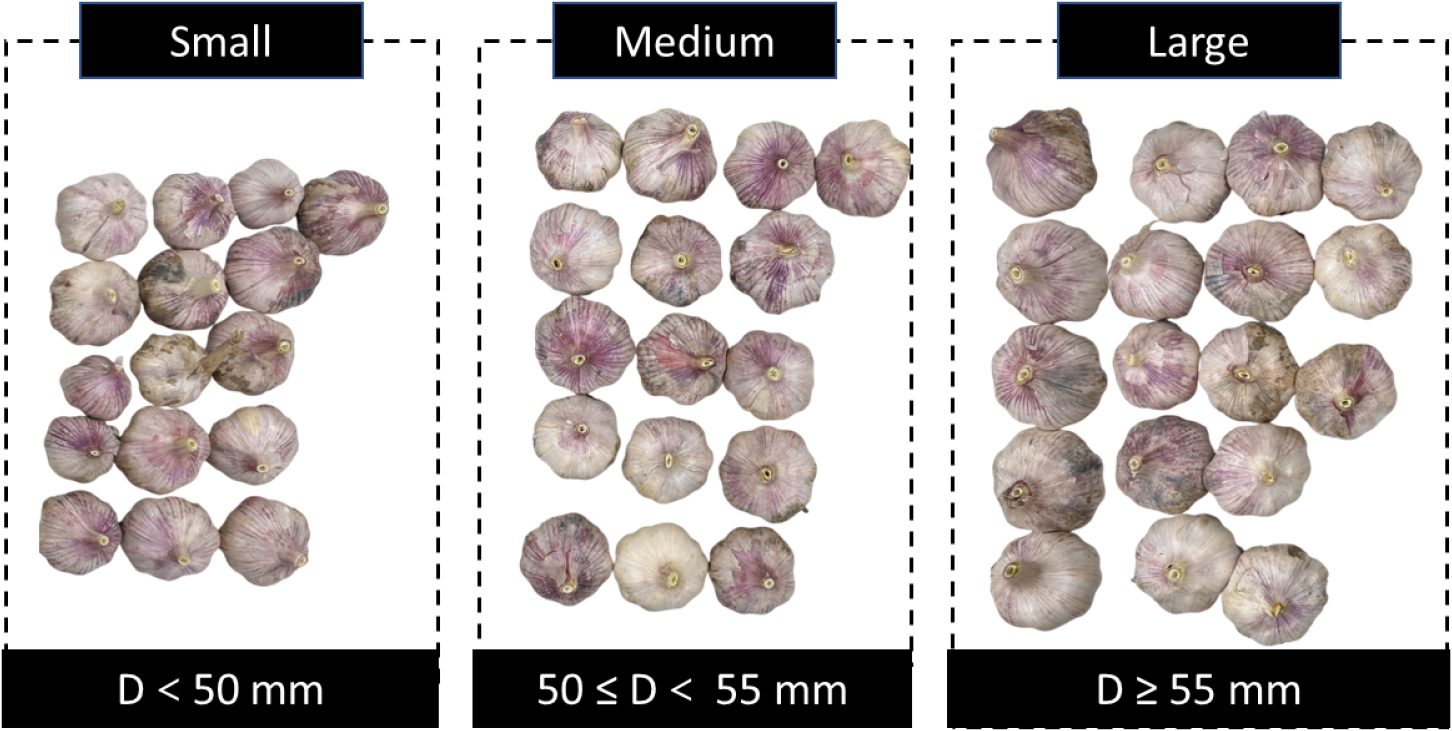
-
Animal
- Genomic characterization of Holstein–Jersey crossbred cattle in Korea using genome-wide SNP data
- Seul Gy Lee, Gyeonglim Ryu, Mi-Na Park, Chang Gwan Dang, Jae Hyuk Jang, Dajeong Lim, Tae-Jeong Choi
- The number of Jersey cattle raised in the Korean dairy industry has been steadily increasing; however, their population size remains small compared …
- The number of Jersey cattle raised in the Korean dairy industry has been steadily increasing; however, their population size remains small compared with Holsteins, and studies on their genetic characteristics are still limited. This study aimed to establish a genetic reference for the Jersey population in Korea by characterizing the genetic structure of domestic Jersey and Holstein populations and quantitatively evaluating changes in breed composition across successive backcross generations (F1 to F6) produced by mating Jerseys to Holsteins. Using the Illumina BovineSNP50 V3 SNP chip, a total of 53,218 SNPs were genotyped, and after quality control, 26,931 SNPs shared among 494 Jersey, 742 Holstein, and 98 crossbred animals were retained for downstream analyses. Principal component analysis (PCA) clearly separated Holstein and Jersey cattle into two distinct genetic clusters, demonstrating substantial genetic differentiation between the breeds. Supervised ADMIXTURE analysis revealed a progressive increase in Jersey ancestry across backcross generations, with mean Jersey proportions of 0.55 in F1, 0.74 in F2, 0.87 in F3, and 0.99 in F4. Notably, animals from the F4 and later generations clustered almost entirely within the Jersey group in the PCA plot, indicating convergence toward a genetic composition effectively indistinguishable from purebred Jerseys. These patterns were consistent with theoretical expectations of backcrossing (F1: 50%, F2: 75%, F3: 87.5%, F4: 93.75%) as well as international criteria for breed purity recognition (e.g., the 7/8 standard of the Canadian Animal Pedigree Act and the U.S. Council on Dairy Cattle Breeding (CDCB) purity threshold of Breed Base Representation (BBR) ≥ 94%). Overall, this study provides a foundational reference population for Jerseys in Korea and establishes an analytical framework for accurately determining breed composition in crossbred cattle. The findings offer essential resources for setting registration criteria for backcross progeny, improving pedigree management, supporting breeding program decisions, and guiding national strategies for genetic resource conservation in the Korean dairy industry. - COLLAPSE
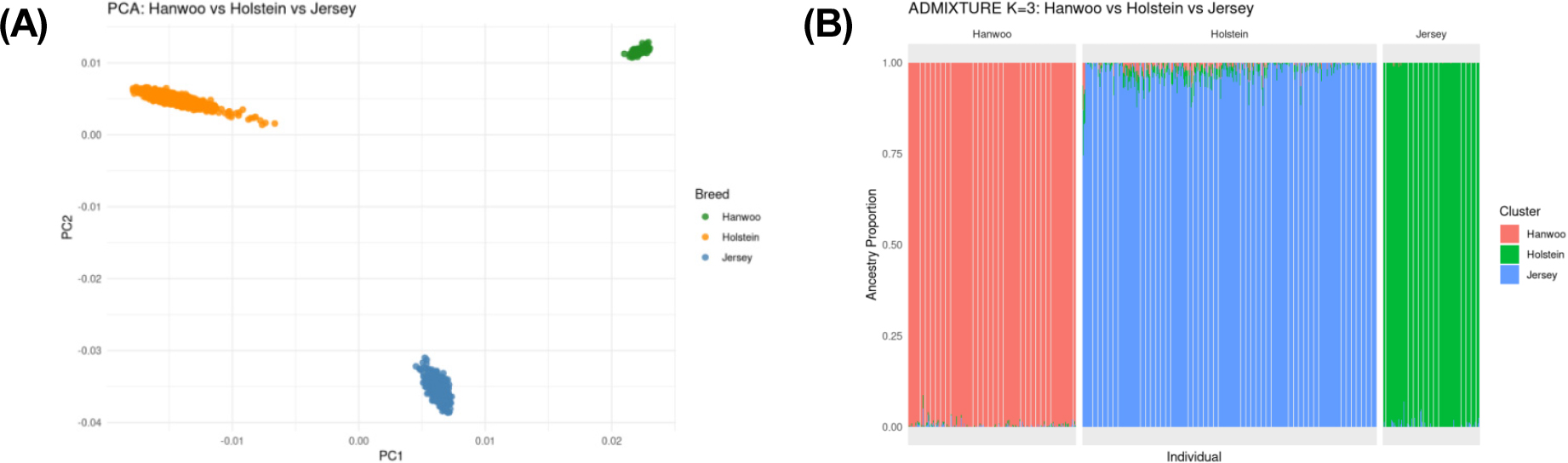
Journal Informaiton
 Korean Journal of Agricultural Science
Korean Journal of Agricultural Science
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Korean Journal of Agricultural Science
Korean Journal of Agricultural Science












