-
Animal
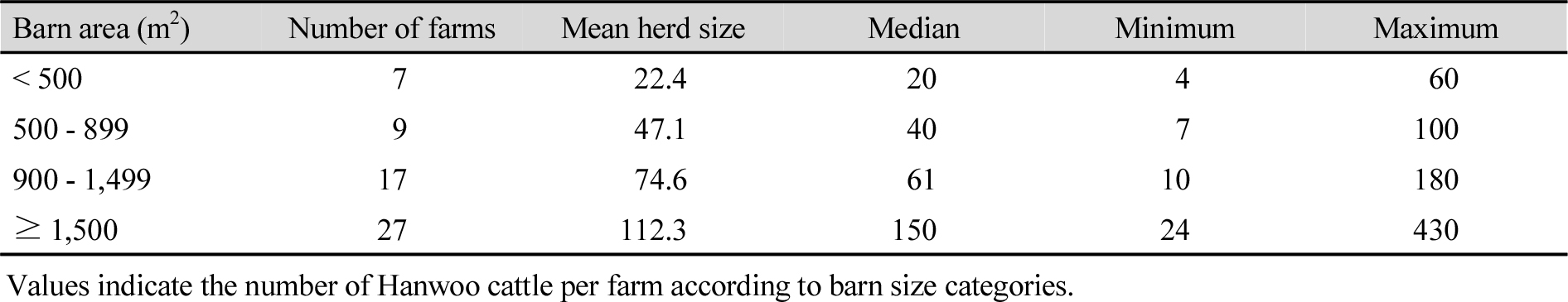
- Management of cattle manure compost, awareness of maturity testing, and distribution by barn size in Hanwoo farms of Gyeongbuk Province
- Soon Hwangbo, Sung Il Kim, Ji-Hong Lee
-
Animal
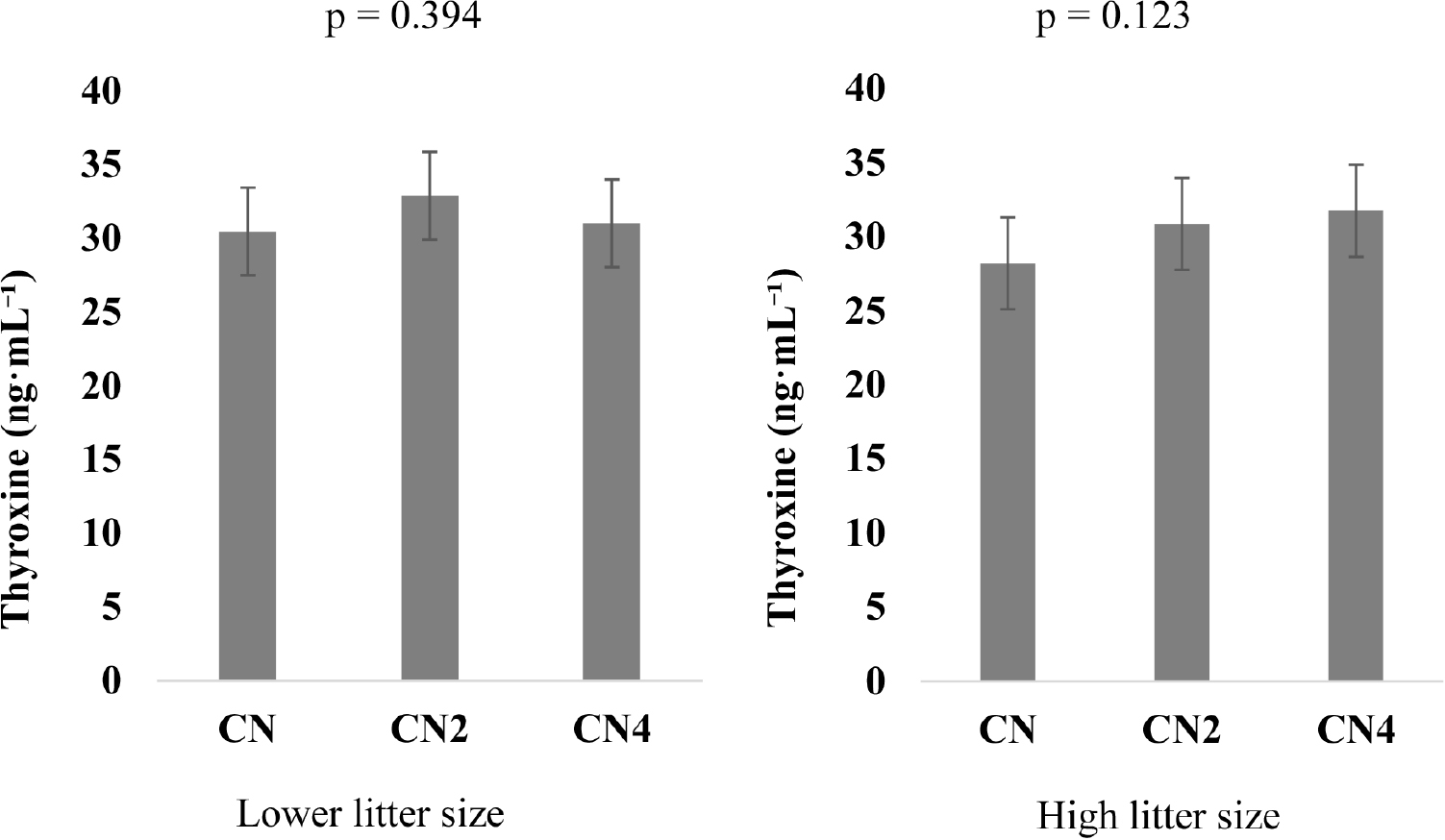
- Effects of L-phenylalanine supplementation on hyperprolific sow and litter performance during lactation
- Elick Njoroge Kinara, Abdolreza Hosseindoust, Jun Young Mun, Habeeb Tajudeen, Sang Hun Ha, Priscilla Neves Silvestre, Jin Soo Kim
-
Animal
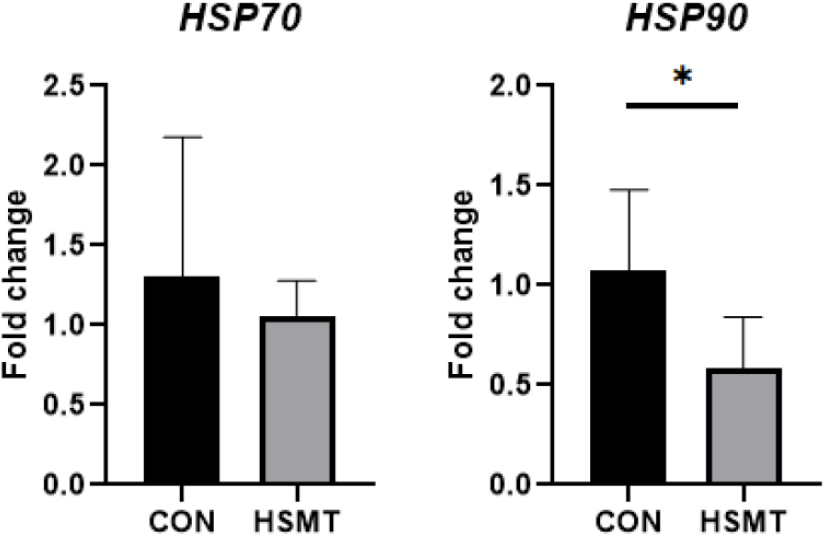
- Effects of a combined nutritional and cooling strategy on productivity and immune responses in heat-stressed Holstein dairy cows
- Byeongcheol Ban, Jaesung Lee, Sungyong Joo, Jihoo Park, Seonho Kim, Mooyoung Jung, Sangsuk Lee, Myunghoo Kim
-
Plant & Forest
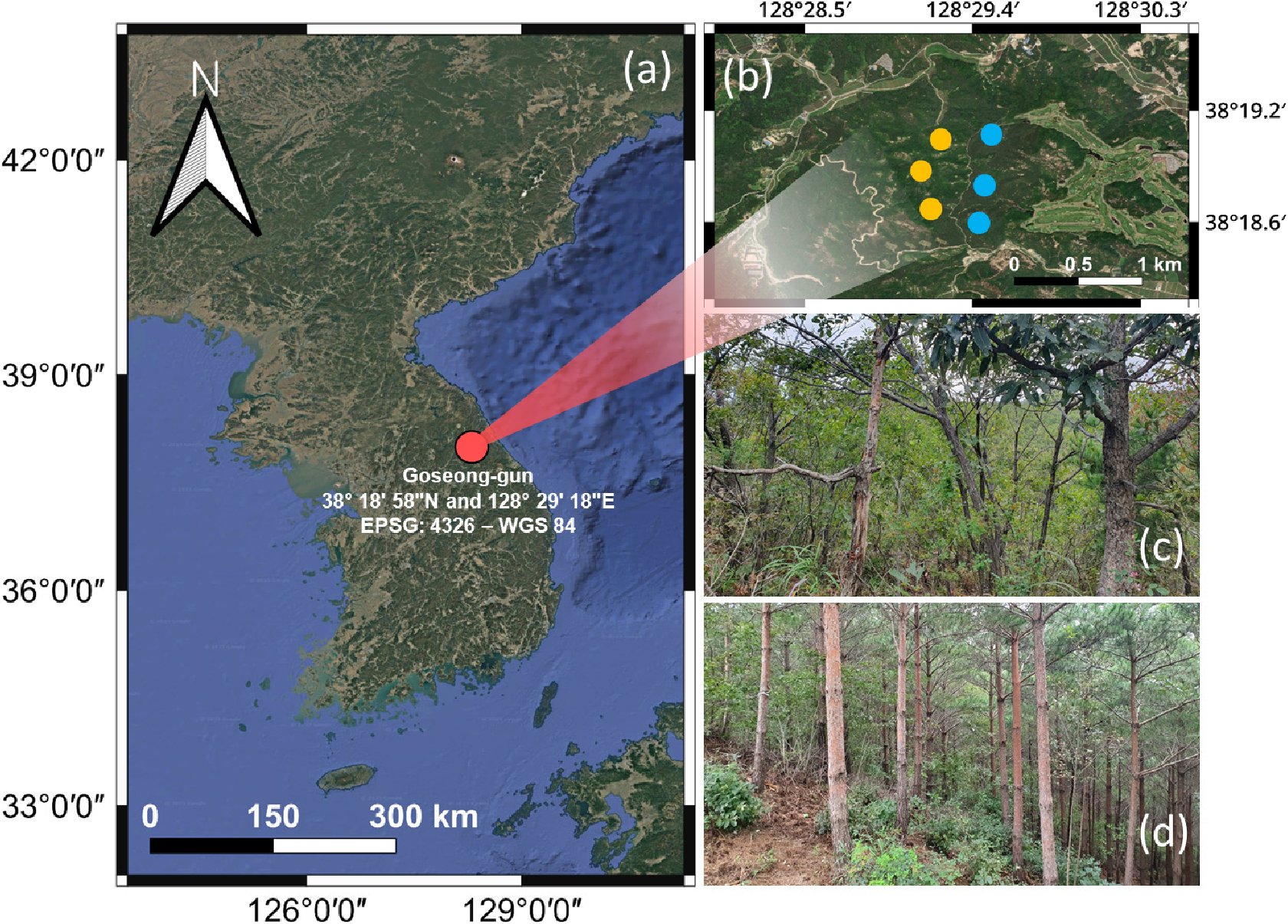
- Effects of natural and planting regeneration on soil properties, forest productivity and economic feasibility 20 years after a forest fire in Goseong
- Si Ho Han, Ji Young An, Woo Bin Youn, Byung Bae Park
-
Animal
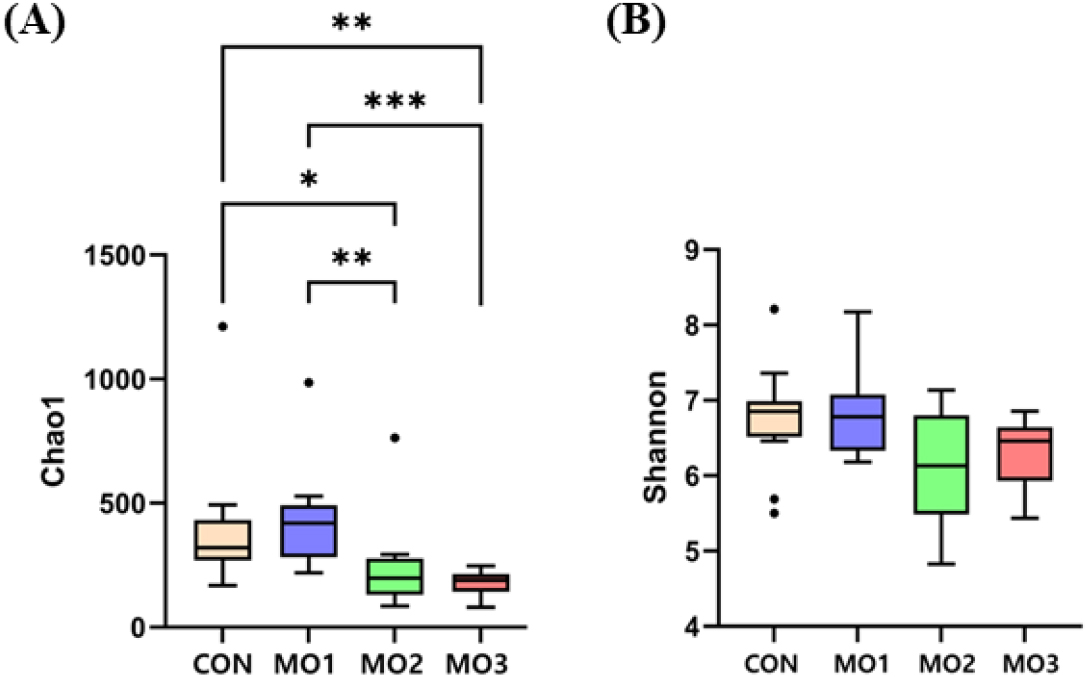
- Dietary monzogranite supplementation affect gut microbiota in weanling pigs
- Jun Young Mun, Abdolreza Hosseindoust, Habeeb Tajudeen, Sang Hun Ha, Yong-Soo Park, So Lim Park, Seong-Il Lim, Jin Soo Kim
-
Food & Chemistry
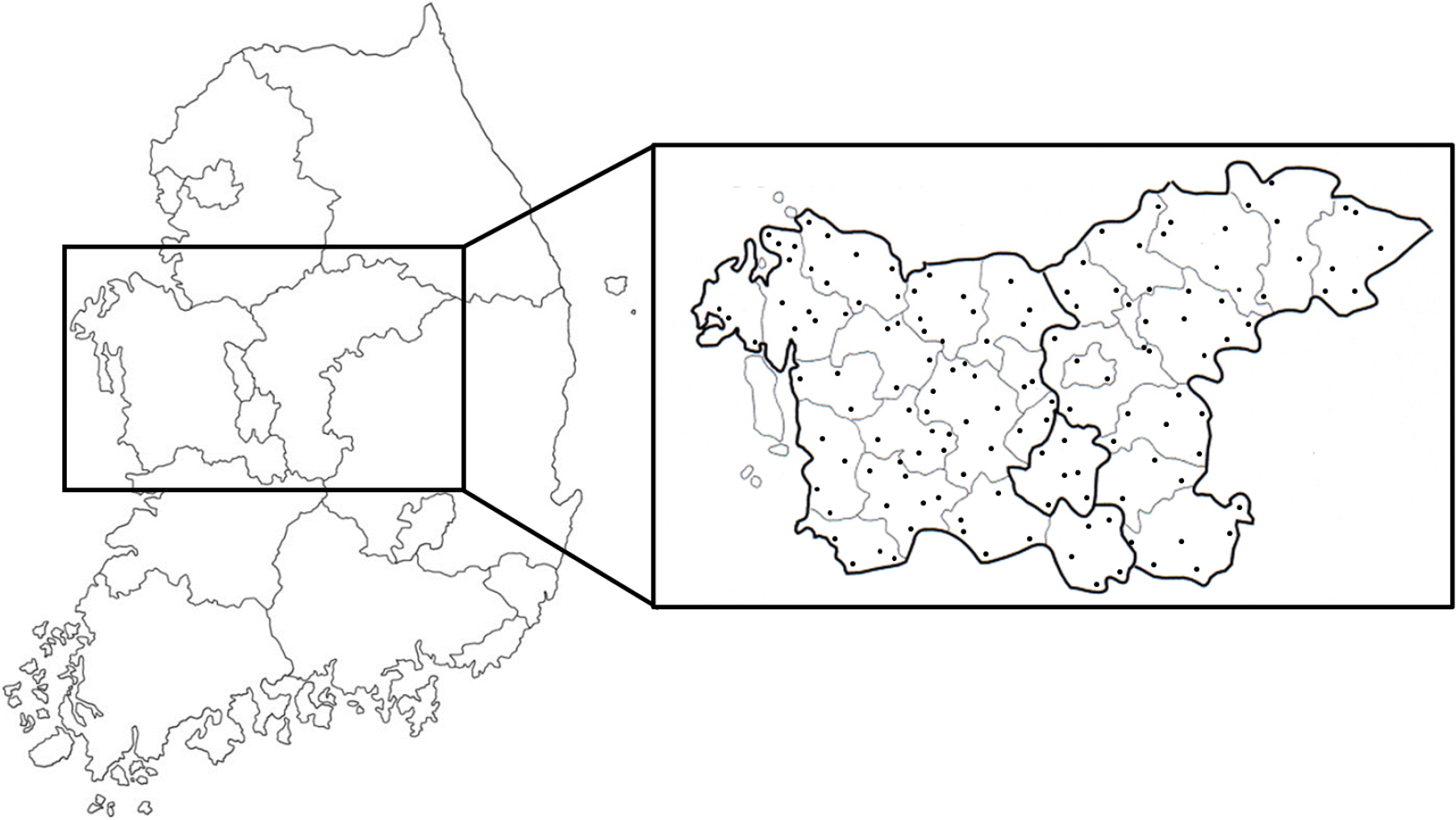
- Combination of soil color information and machine learning technique for rapid quantification of soil organic matter
- Yun-Gu Kang, Jun-Yeong Lee, Jun-Ho Kim, Jiwon Choi, Yong-Jun Kim, Taek-Keun Oh
-
Animal

- Effects of Isulsongi mushroom (Lentinula edodes GNA01) supplementation level and feeding period on serum lipid profiles in dogs
- Eun-Gyeom Jung, Soon Hwangbo
-
Plant & Forest
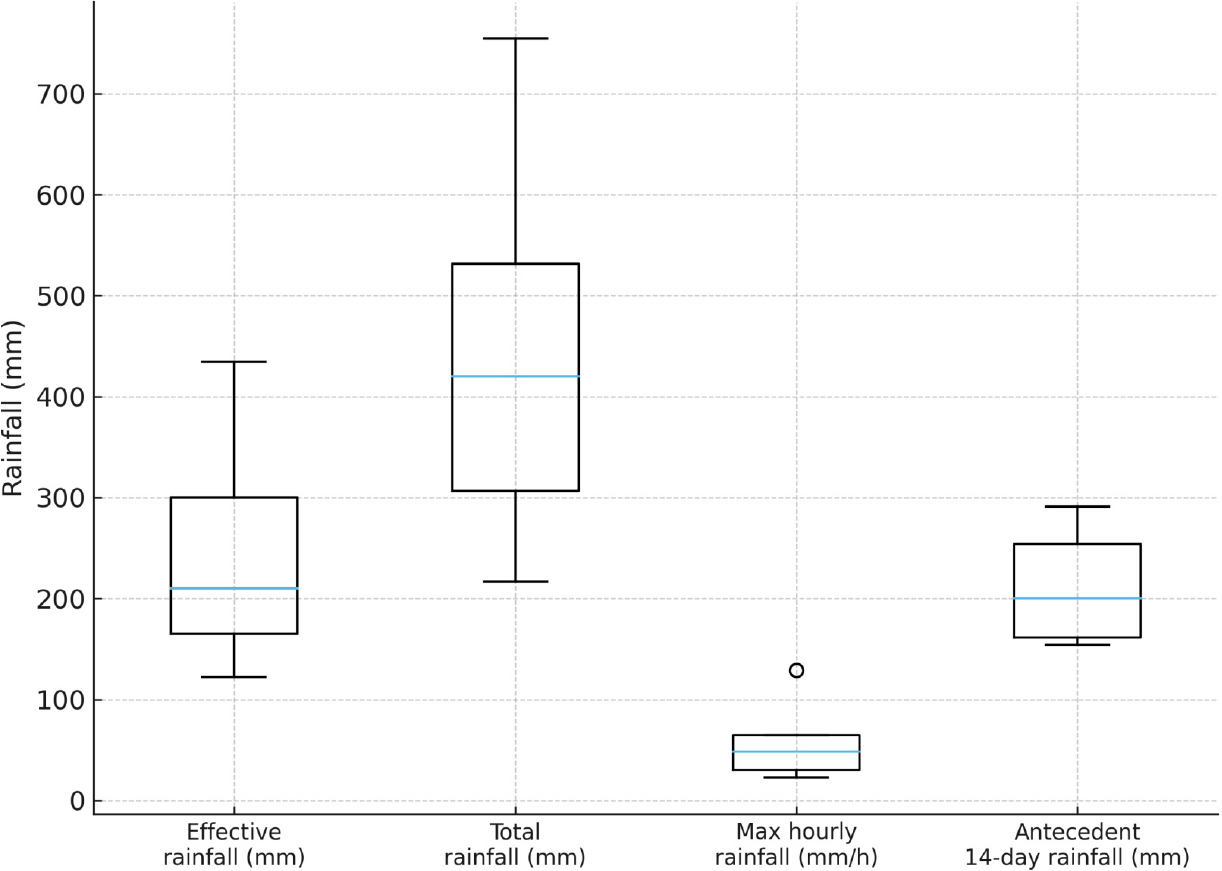
- Analysis of damage characteristics and influencing factors of forest road maintenance
- Seong Man Kim, Ji-Young Son, Hyeongkeun Kwon, Ye Jun Choe, Joon-Woo Lee, Sung-Min Choi
Journal Informaiton
 Korean Journal of Agricultural Science
Korean Journal of Agricultural Science
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Korean Journal of Agricultural Science
Korean Journal of Agricultural Science












